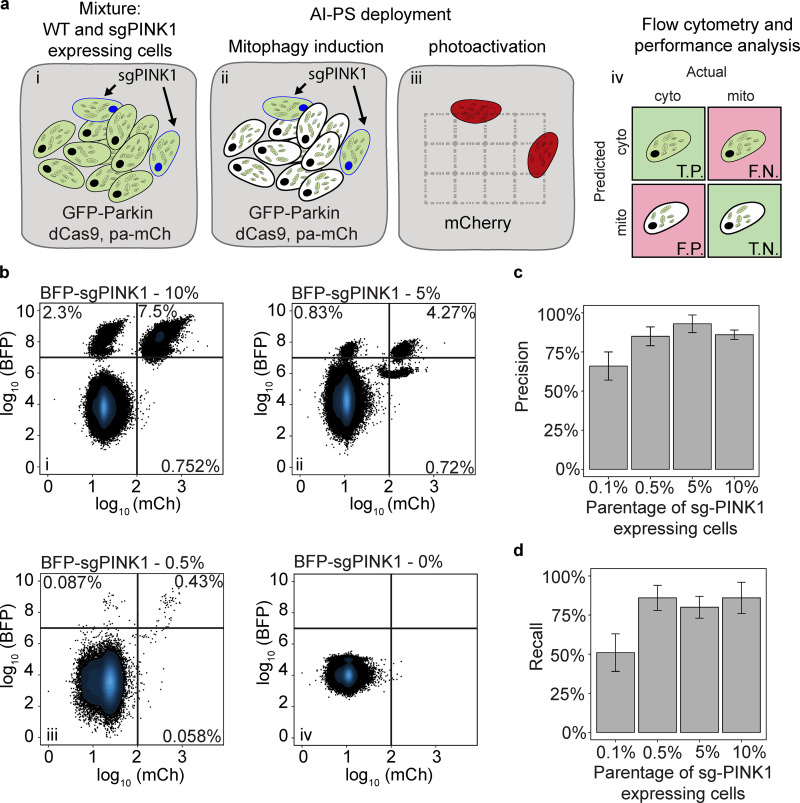
Figure 2.
Performance evaluation of AI-PS flow cytometry sorting. (a) Schematic representation of performance test. i: Mixture of GFP-Parkin cells (black nucleus) and GFP-Parkin cells expressing sgRNA targeting PINK1 (blue nucleus). ii: The color green is concentrated on the mitochondria in WT cells (black nucleus). The color green is dispersed in the cytoplasm of sgRNA-targeting PINK1 cells (blue nucleus). iii: sgPINK1 cells are detected and photoactivated. iv: The detection and flow cytometric separation of the cell populations are evaluated. T.P., true positive; T.N., true negative; F.P., false positive; F.N., false negative. (b) U2OS cells expressing dCas9-KRAB and GFP-Parkin were mixed with 10% (top left), 5% (top right), 0.5% (bottom left), and 0% (bottom left) of the sgPINK1-BFP–expressing cells. Cells with cytosolic GFP-Parkin were automatically called by the AI-PS SVM algorithm and photoactivated. The positive activated cells were gated by the BFP and RFP signals. 200,000 cells were subjected to the AI-PS procedure and the example scatter plot was set on 50,000 cells per condition. n = 3; x-axis mCh signal in log10 scale, y-axis BFP signal in log10 scale. For each scatter plot, the recovered cells are in the upper right gate, missed cells are in the upper left gate, and misclassified cells are in the bottom right. (c and d) Bar graph presenting the precision (c) and recall (d) calculated per condition. mean + SD; n = 3.