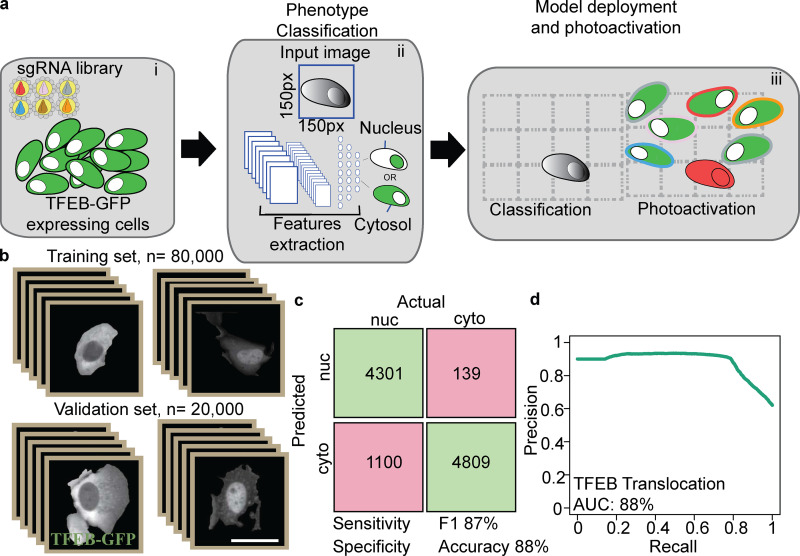
Figure 4.
Deep learning genetic screening platform for TFEB localization. (a) AI-PS screening platform for TFEB translocation. i: Cells were transduced with subpooled sgRNA libraries. ii: Machine learning model. Single-cell images were labeled and trained using CNN classification of nuclear (nuc) TFEB vs. cytosolic (cyto) TFEB. iii: AI-PS deployment. First, cells were imaged and segmented, and then the phenotype of target cells was called and they were photoactivated. (b) Learning set composed of 100,000 single-cell images was used for CNN classification. ImageNet-like CNN architecture was composed of four sets of convolution processes followed by the max pooling procedure. The phenotype decision is based on probability value. A low probability value was assigned to cells with cytosolic GFP-TFEB and a high probability value for cells containing nuclear GFP-TFEB. (c) The CNN classification model was applied on the test set composed of single-cell images of cytosolic or nuclear GFP-TFEB. The confusion matrix was calculated from the test sets, which were collected and pooled from five biologic replicates. Prior to the CNN classification prediction, the images were manually labeled. The green boxes are designated for the true positive single-cell counts (upper left) and the true negative (lower right). The pink boxes represent the false positive single-cell count (upper right) and the false negative (lower left). (d) Precision recall plot summarizes the same image test set. The accuracy is calculated from the precision recall curve. AUC, area under the curve.