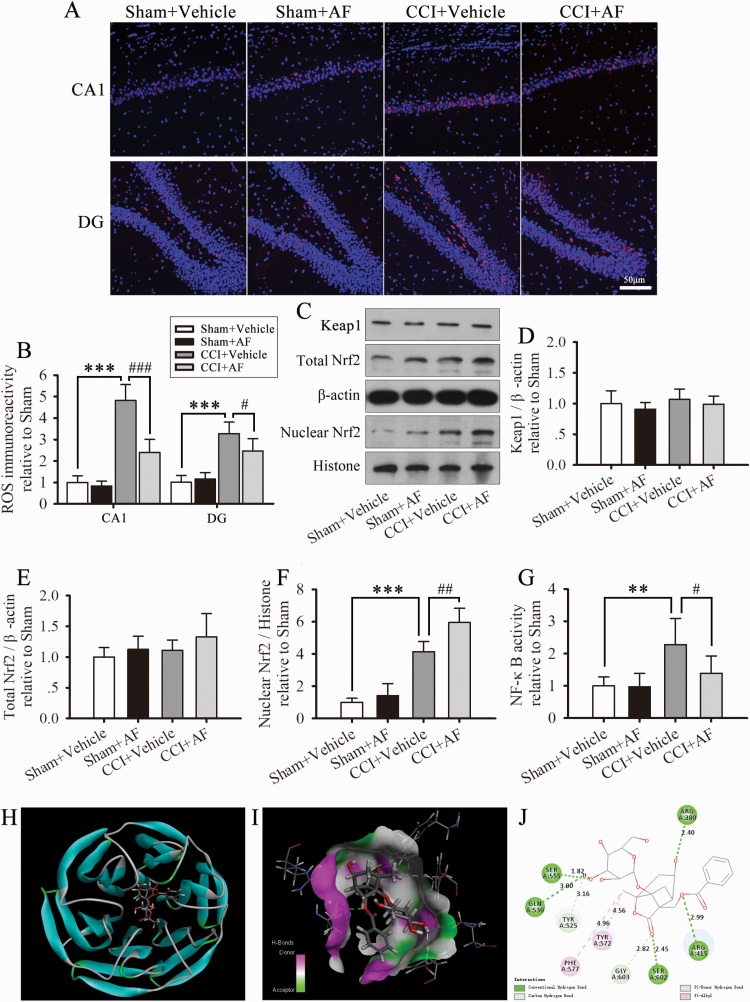
Figure 5.
Albiflorin (AF) promotes Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus and limits the elevated level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and activity of NF-κB in the hippocampus. (A) Representative photographs of hippocampal sections of ROS. (B) Quantification of ROS immunoreactivity in the CA1 layer and dentate gyrus (DG) regions of the hippocampus. (C–F) Western-blot analysis showing the expression of total and nuclear Nrf2 and Keap1 in the hippocampus on day 29 after CCI. The fold changes in the density of total Nrf2 and Keap1 are normalized to that of β-actin, and that of nuclear Nrf2 is normalized to that of histone H3. (G) NF-κB activity. The results are presented as fold changes compared with the sham group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD for n = 4 rats/group; **P < .01, ***P < .001 compared with sham group; #P < .01, ##P < .01 compared with the CCI group. (H–J) Molecular docking of AF to Keap1. (H) KEAP1 Kelch domain in complex with AF (CDOCKER_INTERACTION_ENERGY: -50.142 kcal/mol). (I) Magnified portion of 3D interaction map between AF and 6TYP binding site. (J) 2D diagram of docking structure of AF with 6TYP.