Table 1.
Overview of chemical structures, metabolic precursors, and microbial effects for secondary metabolites that shape the root microbiome
| Secondary metabolite | Example chemical structure | Precursor primary metabolite | Mechanistic action on microbes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoxazinoids |
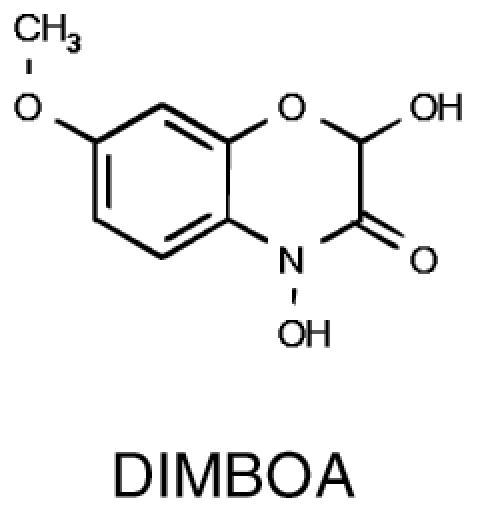
|
• Chorismate | • Chemoattractant (Neal et al., 2012a) • Modification of -SH and -NH2 groups in proteins, leading to enzyme inactivation (Wouters et al., 2016) |
| Camalexin |
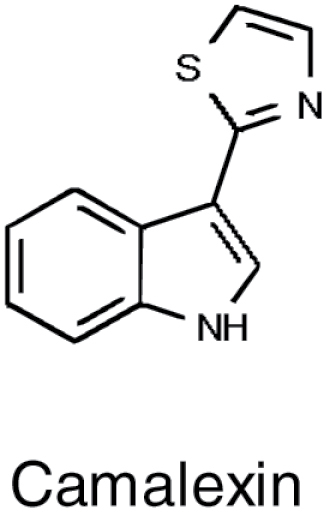
|
• Tryptophan | • Disruption of membrane integrity (Rogers et al., 1996) |
| Coumarins |
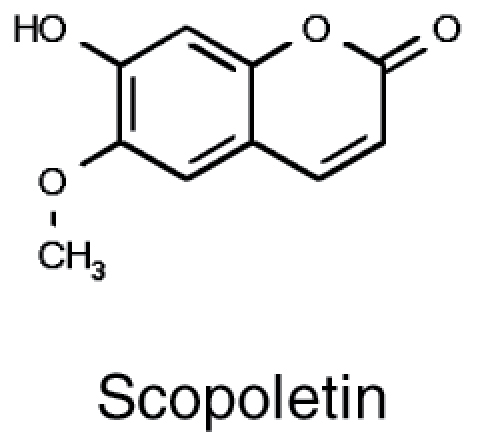
|
• Phenylalanine | • Disruption of transcription (Yang et al., 2016) • Disruption of quorum sensing and biofilm formation (Yang et al., 2016) • Damage to membranes (Yang et al., 2016) |
| Flavonoids |
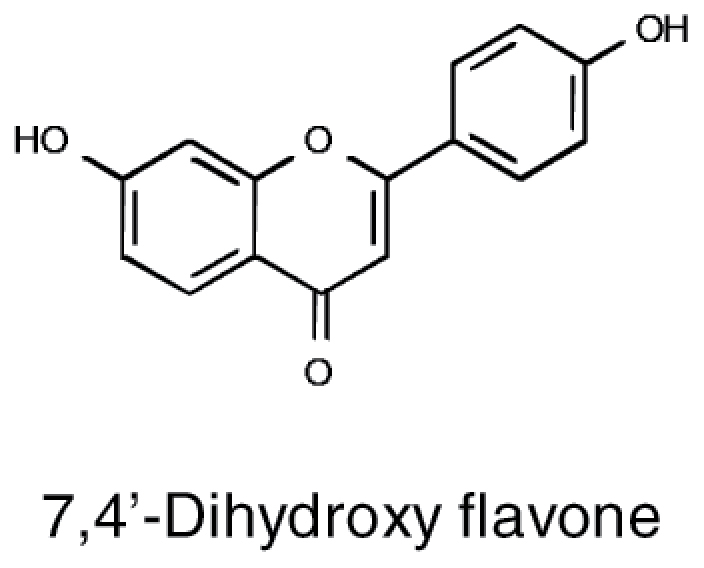
|
• Phenylalanine | • Induction of nod gene expression in Rhizobium (Redmond et al., 1986) • Damage to membranes (Tsuchiya and Iinuma, 2000) • Inhibition of enzymes (Zhang and Rock, 2004) • Disruption of nucleic acid synthesis (Mori et al., 1987) • Disruption of biofilm formation (Vikram et al., 2010) |
| Glucosinolates |
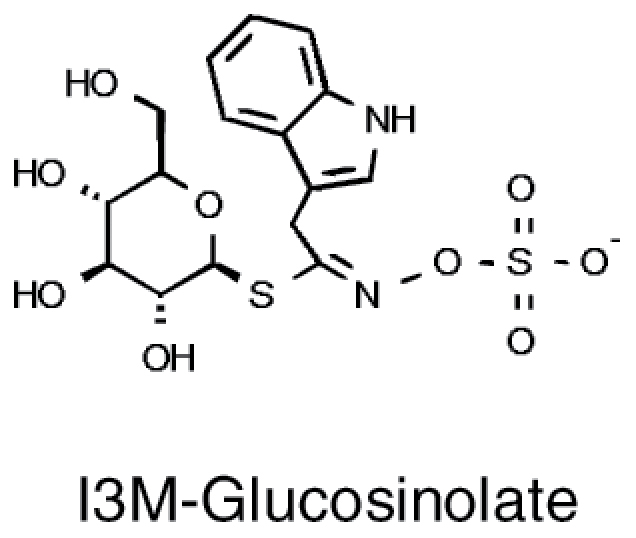
|
• Tryptophan • Phenylalanine • Methionine |
• Isothiocyanate-mediated enzyme inactivation (Aires et al., 2009) • Isothiocyanate-mediated disruption of membrane integrity (Borges et al., 2015) |
| Strigolactones |
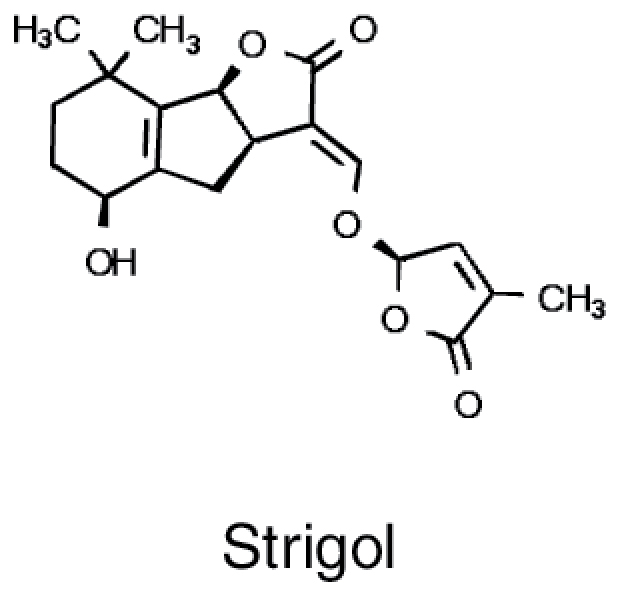
|
• Isopentenyl pyrophosphate • β-Carotene |
• Induction of hyphal branching in mycorrhizal fungi (Akiyama et al., 2005) |
| Triterpenes |
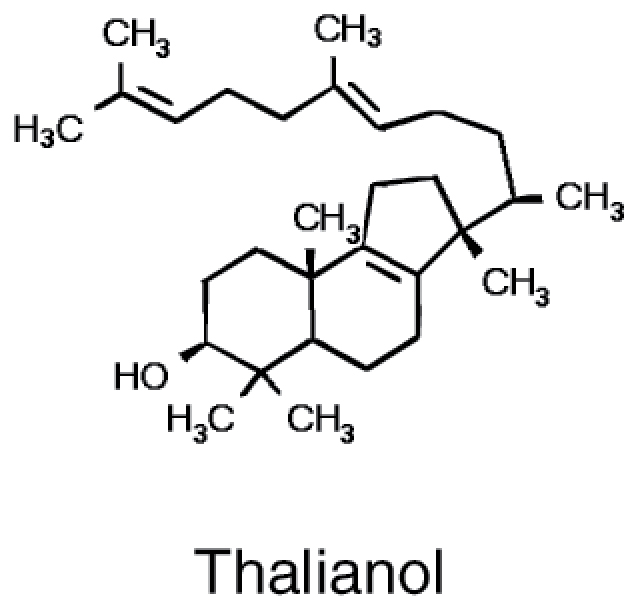
|
• Isopentenyl pyrophosphate • Squalene |
• Disruption of membrane integrity (de León et al., 2010) |
