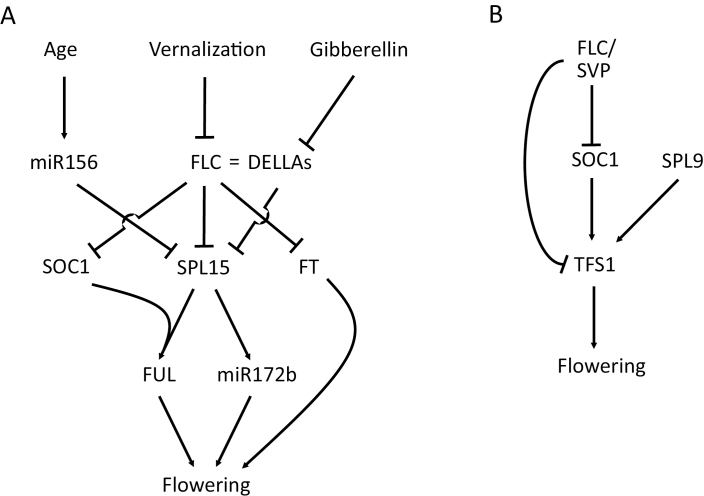
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the gene regulatory network controlled by FLC. (A) FLC is a master regulator of flowering that integrates cues from several flowering pathways in Arabidopsis. FLC expression is repressed by the cold-induced vernalization pathway. FLC directly represses the florigen-encoding gene FT and SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING-LIKE PROTEIN 15 (SPL15). SPL15 is additionally post-translationally regulated by the gibberellin pathway via DELLA proteins and at the post-transcriptional level by the ageing pathway via miR156. The MADS-domain protein SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS1 (SOC1) is encoded by another direct target of FLC, and cooperates with SPL15 to activate target genes such as FRUITFULL and MIR172B. (B) A type II coherent feed-forward loop regulates expression of the positive floral regulator TARGET OF FLC AND SVP1 (TFS1). FLC and SVP directly repress TFS1 transcription and that of its positive activator SOC1. Activation of TFS1 expression in the inflorescence meristem also involves SPL9.