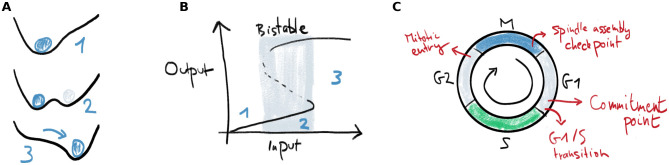
Fig 1. Bistability allows robust switching and is common in the cell cycle.
A) A clear example of bistability in a dynamical system occurs when a little ball moves under the influence of gravity on a hilly terrain. Valleys correspond to stable steady states. These can be created and destroyed under influence of an external parameter. When a steady state disappears, the ball quickly transitions to another steady state. B) Representation of the ball’s position as function of a parameter which determines the shape of the terrain in Panel A. When the input increases beyond a threshold, the left equilibrium position in Panel A disappears and the ball quickly moves to the other stable position. C) In the cell cycle, bistable switches underlie some of the important transitions and checkpoints.