Fig. 2. SUMOylation of ANXA1 promotes OGD/R-induced microglial anti-inflammatory phenotype polarization.
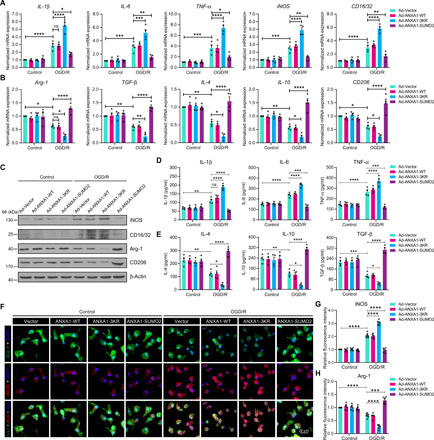
(A and B) SUMOylated ANXA1 but not the WT or the triple mutant of ANXA1 reversed OGD/R-induced mRNA expression of proinflammatory phenotype marker genes (A) and promoted mRNA expression of anti-inflammatory phenotype marker genes (B) in primary cultured microglia, as detected by qPCR. (C) The protein expression of iNOS, CD16/32, Arg-1, and CD206 in primary cultured microglia was examined by immunoblot analysis. (D and E) Expression levels of the cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-4, IL-10, and TGF-β in microglial cell supernatants were detected by ELISA. Quantitative analysis was performed. (F) Immunofluorescence analysis of iNOS (red) and Arg-1 (green) with colabeled DAPI (blue) in primary microglia. Cells were infected with adenoviral vectors carrying WT ANXA1, ANXA1 triple mutant, or ANXA1-SUMO2 and were then treated with OGD for 1 hour and reoxygenation for 24 hours; then, iNOS and Arg-1 were detected by immunofluorescence staining. Scale bar, 20 μm. (G and H) The fluorescence intensity of iNOS (G) or Arg-1 (H) was quantified using ImageJ software. Data in (A), (B), (D), (E), (G), and (H) are presented as means ± SEM and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. ns for P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
