Fig. 3. SUMOylation of ANXA1 suppressed activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in microglia.
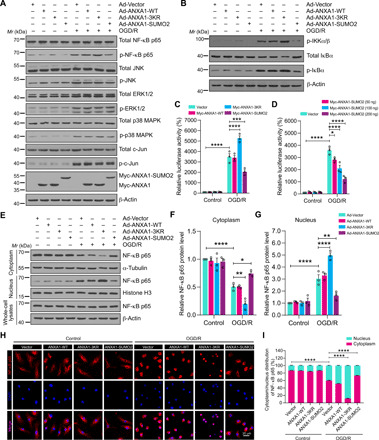
(A) Effects of WT or SUMOylation mutations of ANXA1 overexpression on the activation of the NF-κB and MAPK-AP-1 signaling pathways induced by OGD/R treatment in primary cultured microglial cells. Total protein expression and the phosphorylation levels of NF-κB p65, ERK1/2, JNK, p38 MAPK, and c-Jun were analyzed by immunoblotting. (B) Total protein expression and phosphorylation level of IKKα/β and IκBα in microglial cells were examined by immunoblotting. (C) Dual-luciferase reporter assay results show the transcriptional activity of NF-κB p65 in HEK293T cells. (D) Dual-luciferase reporter assay results show the transcriptional activity of p65 in HEK293T cells treated with increasing doses of ANXA1-SUMO2 (50, 100, and 200 ng). (E) Representative immunoblot analysis of the protein level of NF-κB p65 in cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts of microglia. (F and G) Quantification analysis of the relative amounts of NF-κB p65 protein in cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts. (H) Effects of SUMOylated ANXA1 on p65 nuclear translocation in OGD/R-stimulated microglia. Cells were infected with adenoviral vectors and were then treated with OGD for 1 hour and reoxygenation for 24 hours; then, the localization of NF-κB p65 was detected by immunofluorescence staining. (I) Quantitative analysis of NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation in (H). At least 50 cells per group were counted from three independent experiments. Data in (C), (D), (F), (G), and (I) are presented as the means ± SEM and analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
