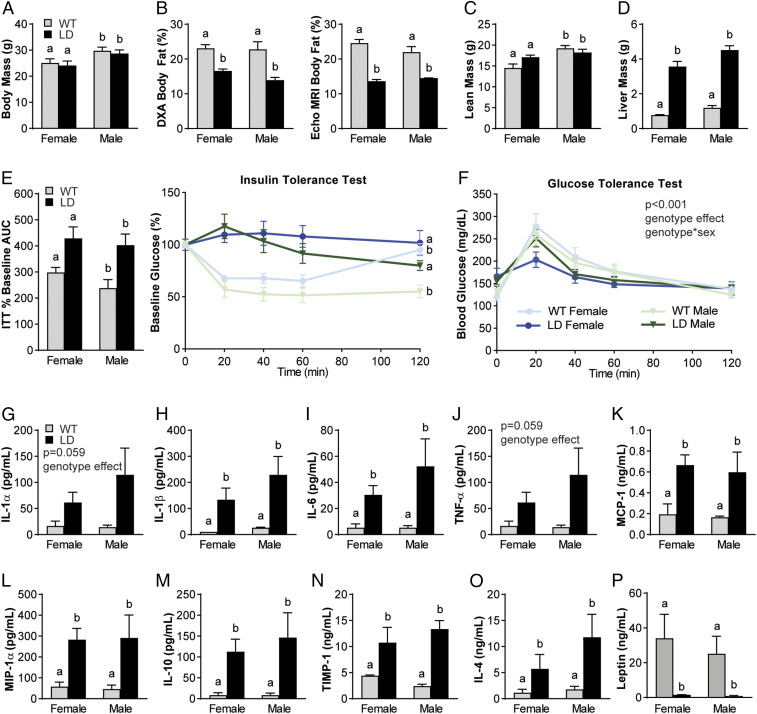
Fig. 1.
Male and female LD mice demonstrate metabolic dysfunction and increased proinflammatory mediators in serum when compared to WT littermate controls. (A–C) LD mice have similar body mass (A) but decreased body fat when measured by DXA and Echo MRI (B) and similar lean mass (C) to same-sex WT littermates. (D and E) LD mice demonstrated increased liver mass (D), insulin-tolerance tests (E, Right), and AUC of insulin-tolerance tests (E, Left). (F) Glucose tolerance demonstrated a significant main effect of genotype and genotype × sex. (G–O) Regardless of sex, LD mice demonstrated increased serum proinflammatory (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, MIP-1α) and increased antiinflammatory mediators (IL-10, TIMP-1, and IL-4) compared to WT littermate controls. (P) LD mice demonstrated near-zero levels of leptin in serum. P < 0.05 between groups is indicated by the letters “a” and “b” (n = 7 to 15 per group for A–F; n = 3 for female WT; n = 4 to 7 for other groups for G–O serum outcomes; analysis by two-way ANOVA with Sidak or Tukey’s post hoc). ITT, insulin-tolerance test.