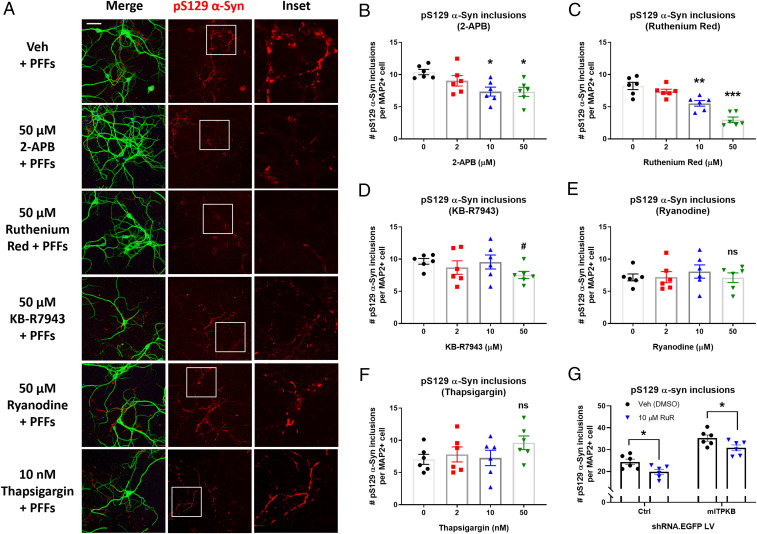
Fig. 5.
Inhibition of the IP3 receptor or mitochondrial calcium uniporter reduces α-syn pathology induced by PFFs. (A) Representative images of pS129 α-syn (red), MAP2 (green), and DAPI (blue) immunocytochemistry of neurons pretreated with vehicle (Veh [DMSO]), 2-APB (IP3R inhibitor), Ruthenium Red (MCU inhibitor), KB-R7943 (MCU inhibitor), Ryanodine (RyR inhibitor), or Thapsigargin (SERCA inhibitor) for 1 h on DIV 9, followed by cotreatment with 2 µg/mL α-syn PFFs for 8 d. (Scale bar, 20 μm.) (B–F) Quantification of the number of pS129 α-syn inclusions per MAP2+ cell in A for cells treated with 2-APB (B), Ruthenium Red (C), KB-R7943 (D), Ryanodine (E), or Thapsigargin (F). #P = 0.2077; *P < 0.05; **P = 0.0011; ***P = 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test; n = 6 wells/group. (G) The number of pS129 α-syn inclusions per MAP2+ cell in Ruthenium Red (RuR)-treated neurons transduced with Ctrl shRNA LV or mITPKB shRNA LV for 11 d. *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test; n = 6 wells/group. The experiments with RuR were repeated four times in independent primary neuron cultures with different plate layouts. The bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM.