Table 1.
Neuroenhancement and mood enhancement—substance classes and pharmacodynamics.
| Substance class | (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/search/search.cgi) | Exemplary active components | Pharmacodynamical targets | Effects for pNE in healthy individuals (from RCTs, see Section 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylxanthine derivatives |
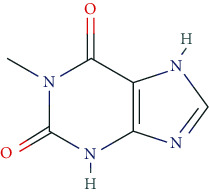
7-Methylxanthine |
Caffeine Theophylline Theobromine |
Adenosine receptor antagonist (A1, A2A, A2B, A3) IP3R1 antagonist RyR1-3 activator cAMP-PDE-inhibitor Ca2+-homeostasis modulator |
Improvement of attention, but not memory and mood |
| Phenylethylamine derivatives |
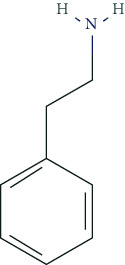
Phenethylamine |
Methylphenidate Dexamphetamine Lisdexamphetamine Methamphetamine Fenetylline Pemoline Ephedrine Norephedrine Levopropylhexedrine Amfepramone Mefenorex Fenfluramine Fenproporex |
DAT and NET inhibitor Facilitation of dopamine and norepinephrine release |
Improvement of attention, but not memory Euphoria in high dose |
| Modafinil |
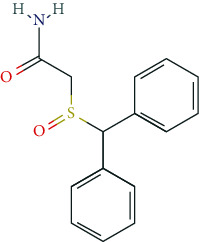
|
DAT and NET inhibitor Modulator of the GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission system |
Improvement of attention, cognition, and mood | |
| Cocaine |
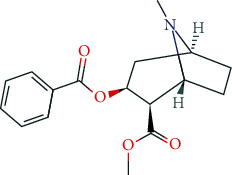
|
DAT and NET inhibitor Serotonin receptor antagonist (5-HT3A, 5-HT3AB) Modulator of the GABAergic and glutamatergic system |
Psychomotor stimulation and euphoria, strongly addictive | |
| Nootropics (antidementia drugs, psychoenergetics) |
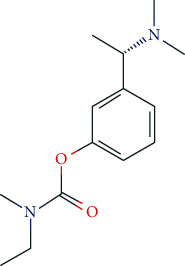
|
Rivastigmine | AChE and BChE inhibitors | No clear evidence of improvement of attention and memory |
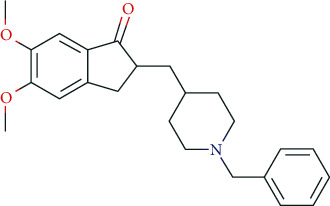
|
Donepezil | AChE inhibitor M1 and M2 receptor antagonist |
||
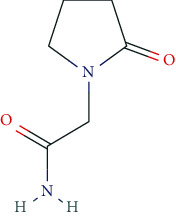
|
Piracetam | GluA1, GluA2, GluA3, GluA4 receptor modulator | ||
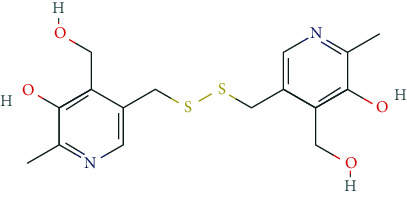
|
Pyritinol | Pyridoxin (vitamin B6) derivate | ||
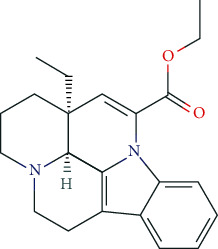
|
Vinpocetine | PDE1A and PDE1C inhibitor VGCC blocker |
||
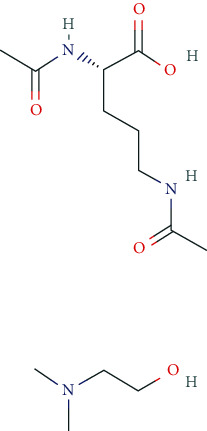
|
Deanol | Precursor of ACh synthesis | ||
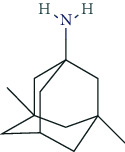
|
Memantine | Non-competitive partial NMDA receptor antagonist | ||
| Ginkgo biloba |
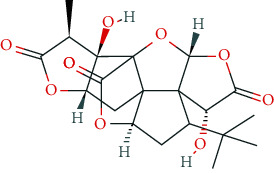
e.g., ginkgolide B |
Flavone glycosides Terpene lactones Sesquiterpene Bilobalide |
Radical scavenger Improvement of cholinergic, dopaminergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission |
Improvement of attention and memory under discussion |
| Benzodiazepines |
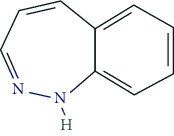
Benzodiazepine |
Bromazepam Diazepam Lorazepam |
Interaction with GABAergic system | Reduction of anxiety and tension |
| Alcohol |
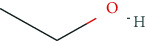
Ethanol |
Ethanol | Interaction with GABAergic, opioid, serotonergic, glutamatergic, and dopaminergic systems | Reduction of anxiety and tension |
| Beta-adrenoceptor antagonists |
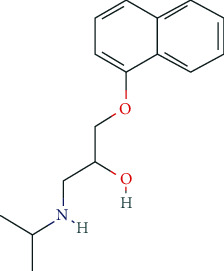
e.g., propanolol |
Propranolol Atenolol Carvedilol |
Blocker of beta-adrenoceptors | Reduction of stress and tension |
| Cannabis |
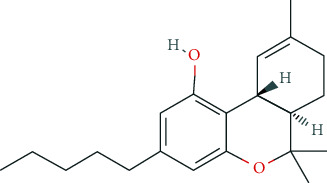
e.g., tetrahydrocannabinol |
Tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabidiol |
Interaction with cannabinoid receptors | Reduction of reduce anxiety |
| Other potential enhancers | Cerebrolysin® (neuropeptides) | Modulation of neurotransmitter systems (e. g., glutamatergic, cholinergic, serotonergic, and dopaminergic) Cotransmitter |
||
|
Montelukast | Leukotriene receptor antagonist | Potential improvement of learning and memory | |
e.g., vitamin A |
Vitamins | Cofactors and coenzymes | No cognitive improvement | |
| Antidepressants—mood enhancers |
e.g., fluoxetine |
Fluoxetine Citalopram Dapoxetine Escitalopram Fluvoxamine Paroxetine Sertraline |
Selective serotonin and/or norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SSRI, SNRI, SSNRI) | No clear evidence of cognitive or mood enhancement |
