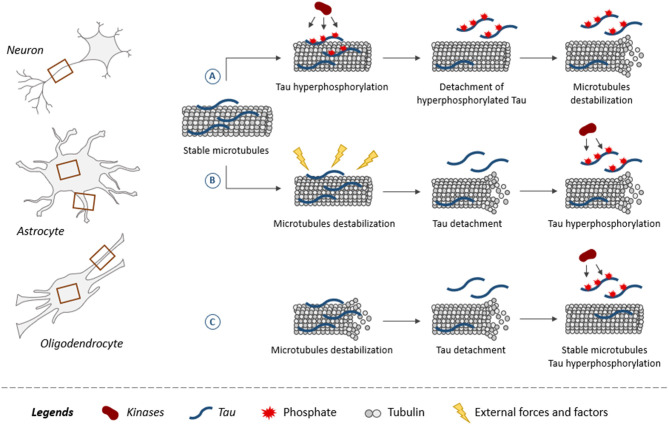
Figure 3.
Role of tau and its phosphorylation in microtubule dynamics. Microtubules, composed of tubulin, are found in both neuronal and glial processes (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes) as indicated by brown squares. Illustration of three scenarios on how tau plays a role in microtubule dynamics within neurons and glial cells. Tau promotes assembly and stabilization of microtubules (A,B). (A) When tau becomes hyperphosphorylated, it reduces its binding to microtubules resulting in its detachment. Microtubules are destabilized upon the loss of tau at their surface. (B) External forces and factors destabilize microtubules, leading to the detachment of tau increasing its access to kinases, which results in its hyperphosphorylation. (C) Tau binding does not stabilize microtubules but instead increases their dynamics. The detachment of tau from microtubules and its hyperphosphorylation is associated with an increase of microtubule stabilization.