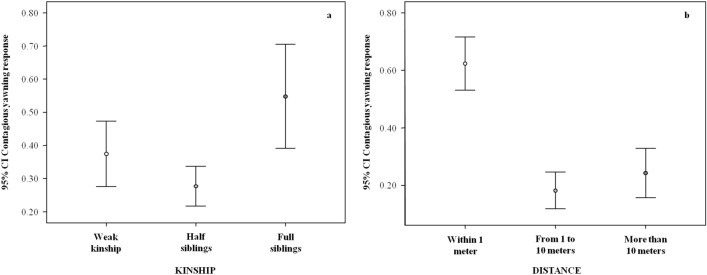
Figure 5.
Error bars (mean, 95% confidence interval) showing the occurrence of yawn contagion (Y axis) as a function of social factors (X axis): kinship (a) and inter-individual distance (b). Both variables have a significant main effect on yawn contagion (results of Model2 included in Table 2), which was highest (a) between full siblings (Tukey post-hoc test with Bonferroni correction, full siblings versus other kinship: 0.031 ≤ p ≤ 0.033; Table 2) and (b) when the distance was within 1 m (Tukey post-hoc test with Bonferroni correction: within 1 m versus other distances: p < 0.05; Table 2). No significant association between the two nominal fixed factors kinship and distance was detected (Goodman and Kruskal’s lambda test: λ = 0.010, T = 0.200, p = 0.841). CI confidence interval.