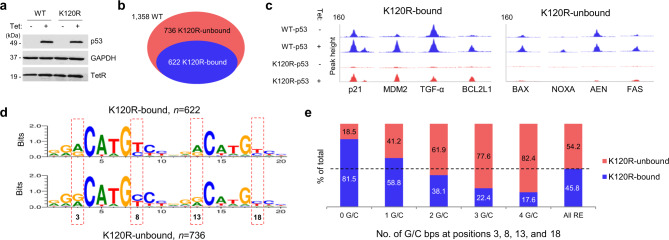
Fig. 1. Differential recognition by p53 of distinct classes of REs is encoded in the G/C vs. A/T bp content at positions 3, 8, 13, and 18 in the RE sequence.
a Representative western blot from three independent experiments showing the expression of WT and K120R-p53 in Tet-inducible H1299 cells. b Venn diagram depicting the number of significantly enriched (with at least 0.3 counts per million [cpm] reads) and previously identified10 WT p53 peaks, which are either bound (blue) or unbound (salmon) by K120R-p53 variant. c UCSC Genome Browser view of WT and K120R-p53 occupancy at selected K120R-bound and K120R-unbound-binding sites. Untreated (−) and Tet-treated (+) tracks for WT and K120R-p53 are shown in blue and salmon, respectively. d Motif analysis of K120R-bound (upper) and K120R-unbound (lower)-binding sites. Red dashed boxes highlight the differences at positions 3, 8, 13, and 18. e Percentage of either K120R-bound (blue) or K120R-unbound (salmon) REs with 0 (n = 178), 1 (n = 374), 2 (n = 501), 3 (n = 254), or 4 (n = 51) G/C bps at positions 3, 8, 13, and 18. The dashed line presents the percentage among all WT p53-binding sites (n = 1358), highlighting an increase in K120R sensitivity with an increase in G/C bp content. Tet tetracycline. TetR tetracycline repressor. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.