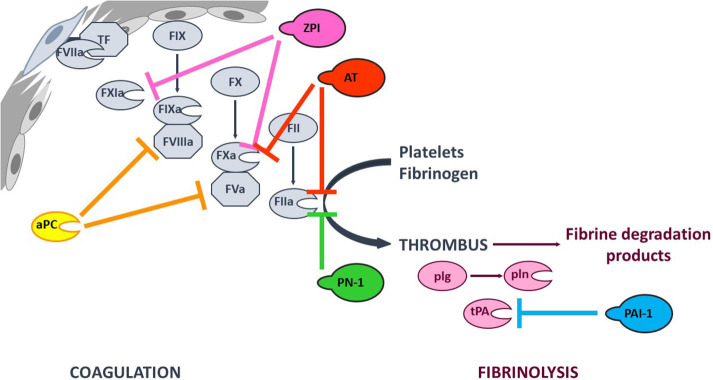
Figure 1.
Simplified overview of the coagulation and fibrinolysis processes. Coagulation is initiated at site of injury by TF-FVIIa complex that activates FIX and FX. FXa catalyzes thrombin (FIIa) formation, that amplifies its own generation by activating FXI and cofactors FVIII and FV. Thrombin also promotes platelet aggregation and fibrinogen into fibrin conversion to form a stable thrombus. Fibrinolysis is triggered once the clot is formed by tPA-induced plasminogen (plg) activation. The resulting plasmin (pln) enzyme is then responsible of fibrin degradation. The targets of the principal anticoagulant and antifibrinolytic serpins, as well as that of anticoagulant aPC are indicated with color capped arrows.