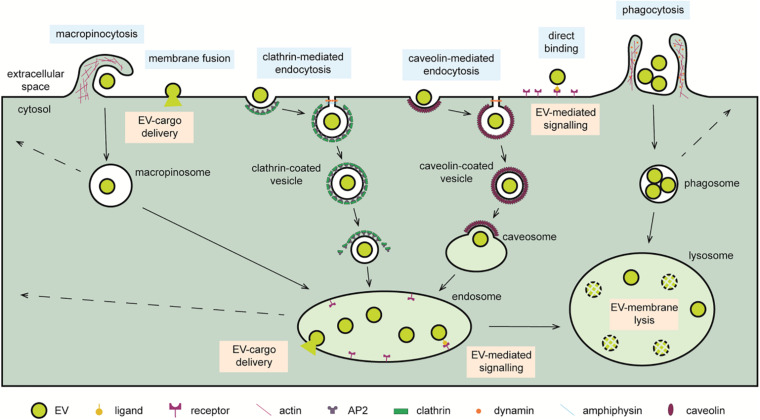
FIGURE 1.
Cellular pathways exploited for the delivery of EV cargo. EVs reaching recipient cells can interact with cell surface receptor or fuse with the limiting membrane and deliver the soluble cargo directly to the cytosol. Alternatively, EVs are internalized through macropinocytosis, micropinocytic processes such as clathrin-mediated endocytosis, and caveolin-mediated endocytosis or phagocytosis. Internalized EVs transit through endosomal compartments when directed to lysosomes. Within endo-lysosomal organelles, ligands present on the EV surface can induce an intracellular signaling cascade through a ligand–receptor mechanism. Moreover, cytosolic delivery of EV cargo may occur by fusion with the membrane of these organelles. The action of acidic hydrolases may liberate the EV cargo for degradation, interaction with other endo-lysosomal components, or recycling to the extracellular milieu by back fusion with the cell membrane. Symbols used are specified in the legend on the bottom of the scheme.