Figure 1.
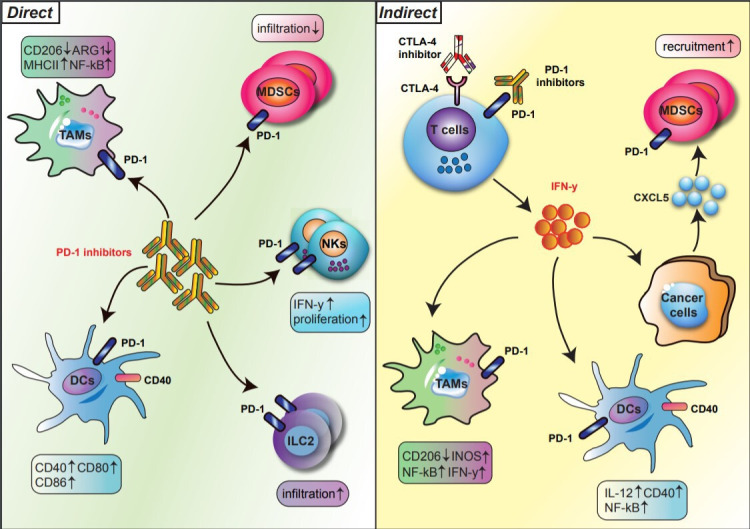
Direct and indirect regulation of innate immune subsets by PD-1 blockade. The regulation of innate immune cells by PD-1 blockade is divided into direct (left) and indirect (right) pathways. In the direct pathway, PD-1 blockade reshapes the phenotypes and functions of innate immune subsets, such as TAMs, DCs, MDSCs, NK cells, and ILC2s, expressing PD-1 (left). In the indirect pathway, T cells activated by anti-PD-1 secrete IFN-y, which in turn phenotypically polarizes myeloid cells within the TME (right). Bold arrows indicate interactions. DCs, dendritic cells; IFN-y, interferon gamma; ILCs, innate lymphoid cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells: NK, natural killer cells; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; TEM, tumor microenvironment.
