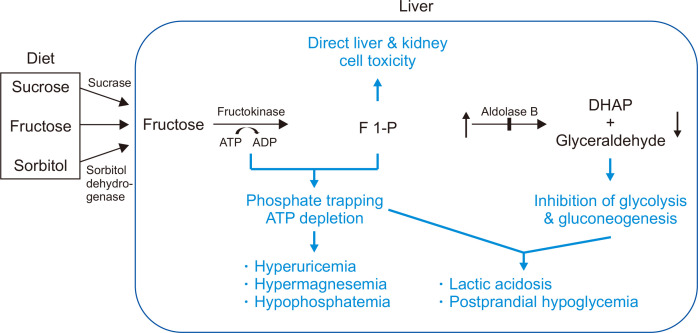
Fig. 1.
Pathophysiology of hereditary fructose intolerance (HFI). Deficiency of aldolase B leads to the accumulation of fructose 1-phosphate (F 1-P), which causes direct toxicity to the liver and kidney. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are downregulated due to the inhibition of DHAP and glyceraldehyde, which enters the pathway. Moreover, ATP is depleted as phosphorylation continues, blocking all processes requiring ATP.
ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate.