Figure 3.
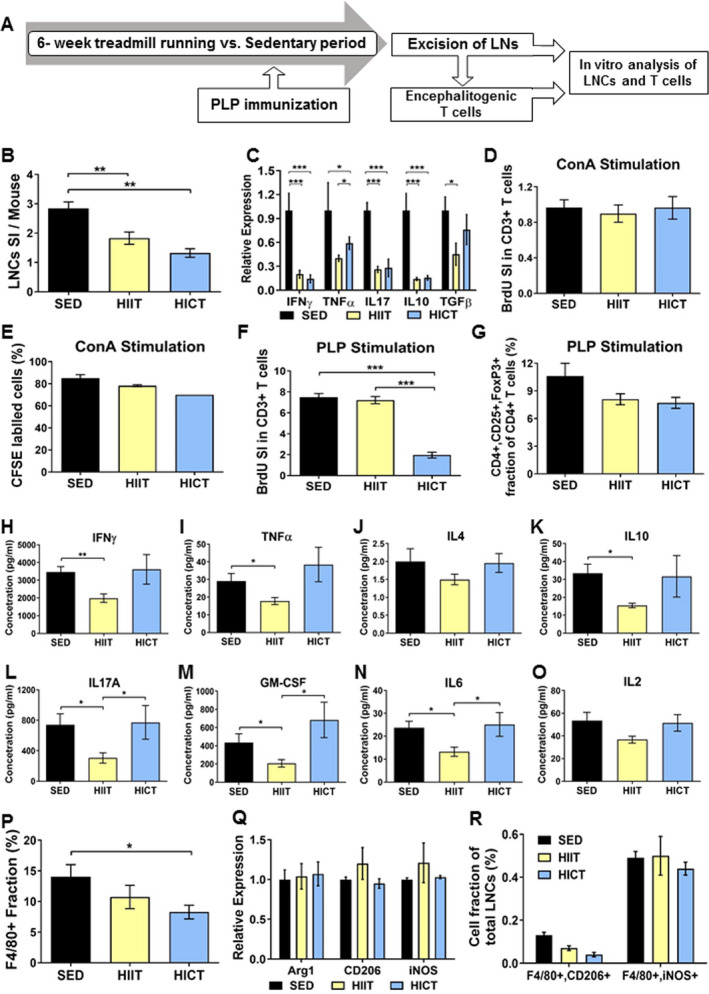
Distinct immuno‐modulatory effects of high‐intensity continuous and interval training on lymph node cells (LNCs), T cells, and macrophages derived from proteolipid (PLP) immunized mice. A: PLP‐ stimulated lymph node cells (LNCs) were excised from high‐intensity interval trained (HIIT), high‐intensity continuous trained (HICT), and sedentary (SED) mice at 10 days post PLP immunization and were stimulated in vitro for 72 h with PLP peptide or concanavalinA (ConA, n = 5‐8/group/experiment). B: Number of LNCs per mouse at day of LNs excision represented by stimulation index (SI): The number of LNCs in the experimental group divided by the number of LNCs in naïve, non‐immunized mice (n = 3). C: Cytokine mRNA levels in LNCs at day of LNs excision for interferon (IFN)‐ γ, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)‐ α, interleukin (IL)‐17, IL‐10 and transforming growth factor (TGF)‐β. Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation into CD3+ T cells at 72 h after ConA (D) or PLP (G) stimulation in vitro, represented by SI: The fraction of CD3+ BrdU+ T cells in the experimental group divided by the fraction of CD3+ BrdU+ T cells in naïve, non‐immunized mice. E: 5(6)‐carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) labeling at 72 h after ConA stimulation in vitro. F: CD4+, CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells at 72 h after PLP stimulation in vitro, represented as cell fraction of total T cells. H‐O: protein concentrations of IFNγ (H), TNFα (I), IL‐4 (J), IL‐10 (K), IL17A (L), granulocyte‐macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF, M), IL‐6 (N) and IL‐2 (O) in supernatants of PLP‐stimulated T cell cultures from PLP‐immunized HIIT, HICT and SED‐ mice. P: F4/80+ macrophage fractions of total LNCs at 72 h after PLP stimulation in vitro for. Q: mRNA levels of arginase (Arg)‐1 and CD206 M2 macrophages phenotype markers and inducible nitric oxidase synthase (iNOS) M1 type macrophages marker at 72 h after PLP stimulation in vitro. R: F4/80+, CD206+ M2 macrophages and F4/80+,iNOS + M1 macrophages fractions out of total LNCs population at 72 h after PLP stimulation in vitro. In response PLP immunization: (1) HICT induced reduction in the number of LNCs (B) and mRNA levels of cytokines (C) on day of LNs excision, and T cell proliferation (G) and number of macrophages (P) in response to PLP stimulation in vitro. (2) HIIT induced reduction in the number of LNCs (B) and mRNA levels of cytokines (C) on day of LNs excision, and Th1 (H, I), Th17 (L, M) and pro‐inflammatory IL6 (N) cytokines secretion in response to PLP stimulation in vitro. (3) Neither HICT nor HIIT affected the fraction of regulatory T cells (F), Th2‐ derived IL4 (J) and IL2 (O) cytokines secretion and macrophages phenotype (Q, R) after 72 h of PLP stimulation in vitro. (4) Training did not affect proliferation (D) and division cycles (E) of T cells in response ConA non‐specific stimulation. Data are mean ± SE. G, P: Relative expression to SED group = 1. * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
