FIGURE 40.
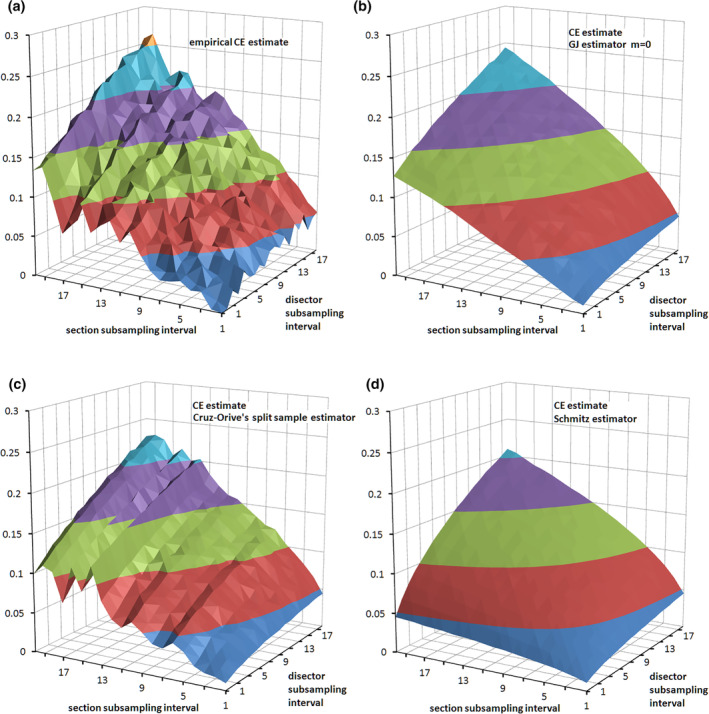
Empirical CE estimates and CE estimators. In (a), CEs of a number estimate were estimated empirically by collecting a very large data set from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells (Slomianka & West, 2005). From this data set subsamples were drawn and the CEs were estimated (CV of the mean of all subsamples for each combination of subsampling intervals). The Gundersen–Jensen (GJ) estimator (b) and Curz–Orive's split sample estimator (c) provide useful approximations of the variance generated by the sampling. The estimator of Schmitz (1998) (d) considers only the variance component generate by sampling within sections and provides a simple to calculate, rough‐and‐ready estimate if the sampling of sections contributes very little variance to estimates [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
