Figure 1.
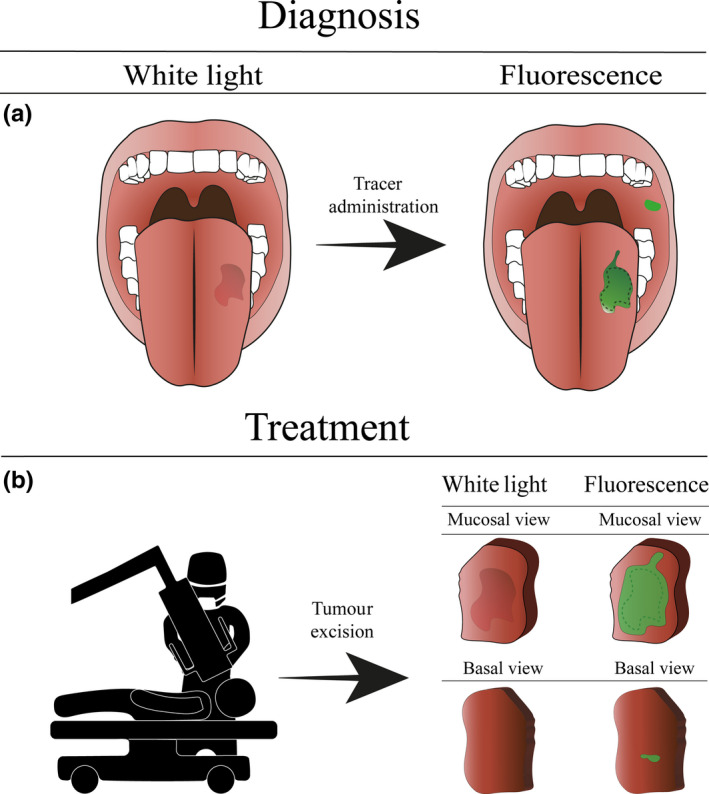
Schematic using fluorescence imaging for oral squamous cell carcinoma detection. (a) The diagnostic procedure in oral squamous cell carcinoma treatment. The fluorescent agent is topically administered to the patient. Due to the topical administration, the fluorescent signal can be detected immediately to assess the lesion and guide biopsy. Note that additional lesions otherwise missed by standard of care can be visualised. (b) Intraoperative margin assessment using ex vivo fluorescence imaging. Directly after excision, the margins of the excised specimen are scanned to identify tumour‐positive resection margins and enable immediate re‐resection
