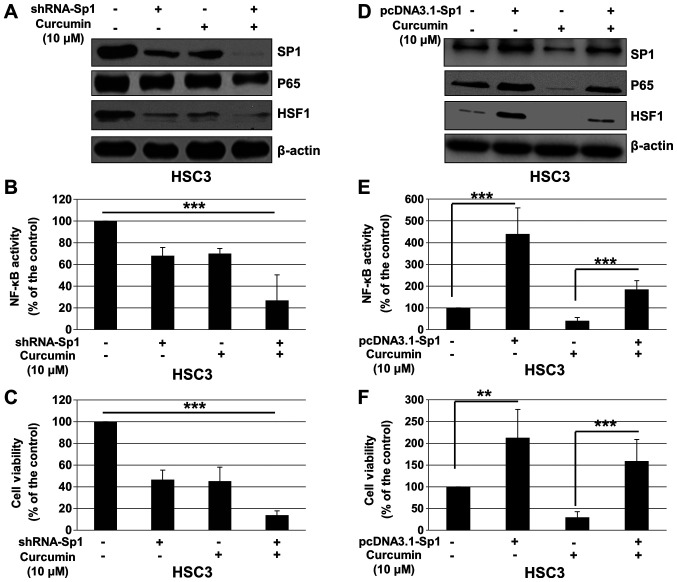
Figure 5.
Cur inhibits cell proliferation and NF-κB activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells in a Sp1-dependent manner. HSC3 cells were transfected with control RNA or shRNA-Sp1 for 4 h, followed by treatment with Cur (10 µM) for 48 h. (A) Expression of Sp1, p65 and HSF1 was detected by western blotting after 48 h treatment. (B) NF-κB activity was determined using a Dual-Luciferase reporter assay system at 12 h. (C) Cell viability was determined by a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay after 24 h treatment. HSC3 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-Sp1 for 4 h, followed by treatment with Cur (10 µM) for 48 h. (D) Expression of Sp1, p65 and HSF1 was detected by western blotting after 48 h treatment. (E) NF-κB activity was determined using a Dual-Luciferase reporter assay system at 12 h. (F) Cell viability was determined by a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay after 24 h treatment. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. control group. Cur, curcumin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; Sp1, specificity protein 1; HSF1, heat shock factor 1; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.