Figure 3. Experimental data from studies indicating that SkM and CM proteins are essential for enhancing prothrombin activation.
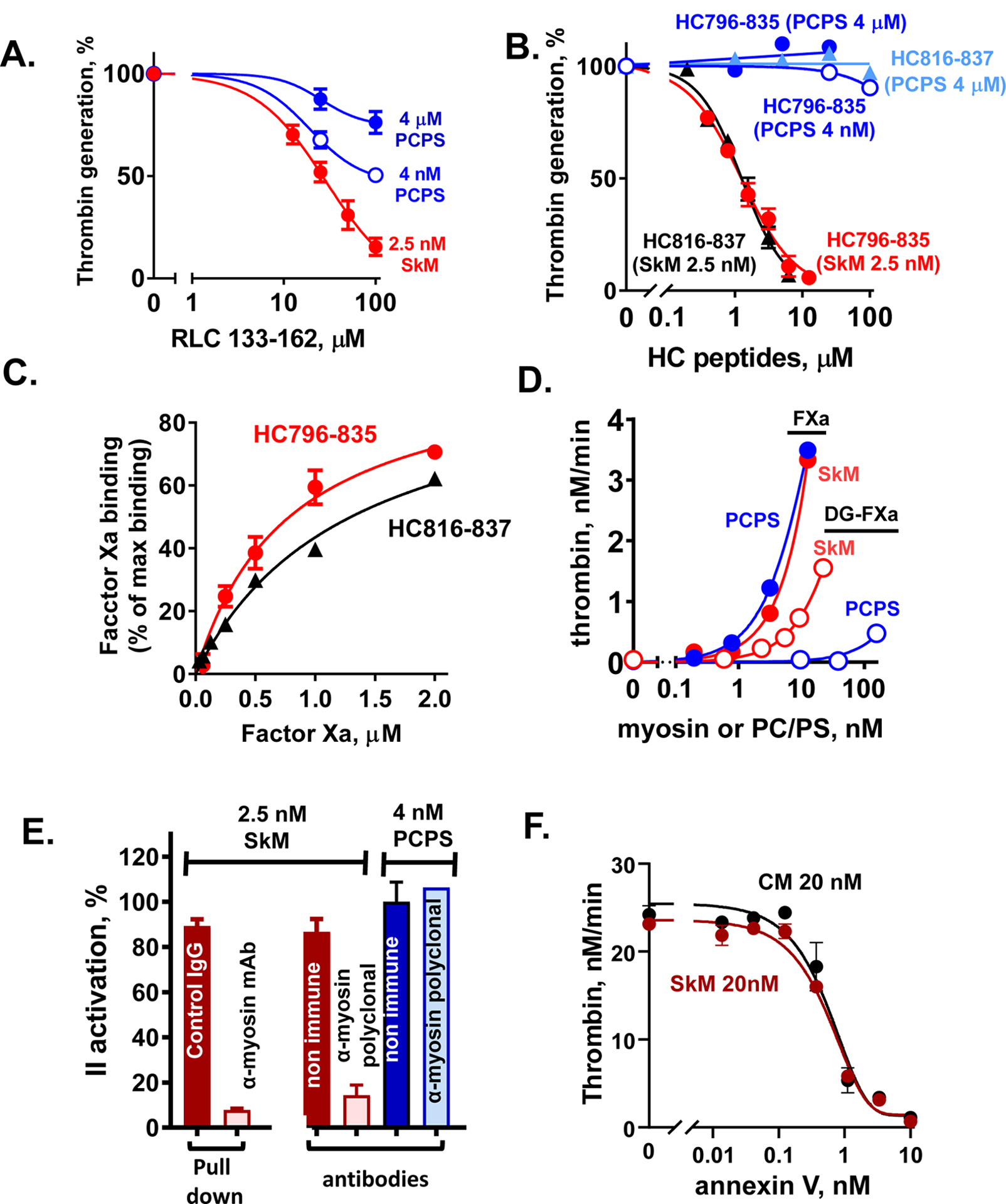
(A, B) Inhibition of myosin-enhanced or phospholipid vesicle-enhanced prothrombin activation by SkM-sequence based peptides (RLC133–162 (A) and HC796–835 and HC816–836 (B)) was studied in the presence of SkM (2.5 nM, final) or phospholipid vesicles (PC/PS, 80%/20% w/w) (4 μM or 4 nM, final) as described [24]. Thrombin generation was determined as described [24]. 100 % was the value thrombin generation for controls in the absence of added peptides. (C) The binding of FXa, as determined using FXa chromogenic activity assays, to immobilized HC peptides was tested as described [24]. Each value represents the mean [SD] of at least triplicate determinations. (D) The effect of varying concentrations of SkM or of PC/PS (80%/20%) vesicles on the initial rate of prothrombin activation by FXa or Gla domain-less FXa (DG-FXa) (0.2 nM, final) was determined as described [14]. (E) Anti-myosin antibodies were used to pull-down SkM from solution or to block myosin’s procoagulant activity, as described [14]. From left to right, 2 studies are depicted. First, immobilized mAb-MF20 removed > 90 % of SkM’s procoagulant activity from solution vs. control non-immune IgG. Second, polyclonal anti-myosin antibodies in solution blocked > 80% of SkM’s procoagulant activity vs. controls (two red bars), and there were no significant effects on the procoagulant activity of PC/PS vesicles by anti-myosin or non-immune IgG’s (two blue bars). (F) The effects of varying concentrations of annexin V on the initial rate of prothrombin activation by FXa/FVa in the presence of SkM (closed symbols) or CM (open symbols) (each at 20 nM final) were determined. Annexin V was incubated with FVa (2.4 nM, final) and FXa (0.2 nM, final) in Tris-buffered saline, 0.5% BSA plus 5 mM CaCl2 with SkM or CM, and thrombin generation was initiated by adding prothrombin (0.75 μM, final). After 5 min, quenching was made with EDTA (10 mM, final) and thrombin formation was quantified. For all studies described in this figure, as for our published studies [13–16, 24, 25], the SkM or CM preparation was dissolved in water and then immediately dialyzed into Tris buffer (pH 7.4) containing 0.6 M NaCl at 4°C. After dialysis, particles causing turbidity were removed by high speed centrifugation (21,130xg for 1 min) which removed visible aggregates.
