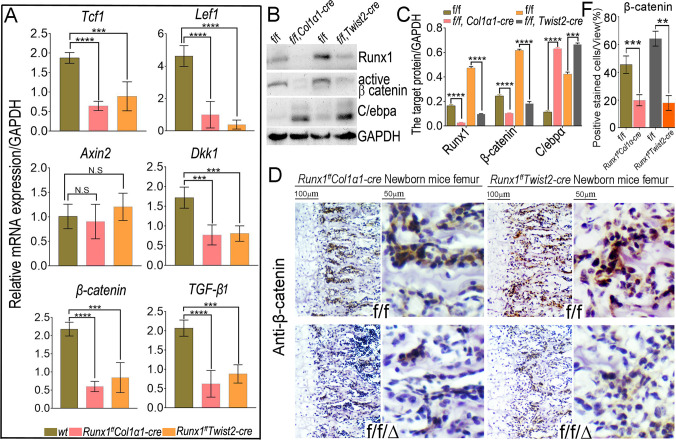
Fig 10. Runx1 deficiency impairs β-catenin signaling in vivo and in vitro.
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of lef1, tcf1, axin2, dkk1, β-catenin and TGF-β expression normalized by GAPDH. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of Runx1, β-catenin and C/ebpa protein level in both Runx1-deficient cells compared with their control cells. (C) The quantitative data analysis for the Runx1, β-catenin and C/ebpa protein levels normalized to GAPDH in B. (D) IHC staining of active β-catenin in Runx1-deficient mice femurs compared with their controls. (E) The quantitative data analysis for β-catenin level in the Runx1-deficient mice femurs compared with their controls. The data were presented as mean ± SD, n = 4. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NS, not significant.