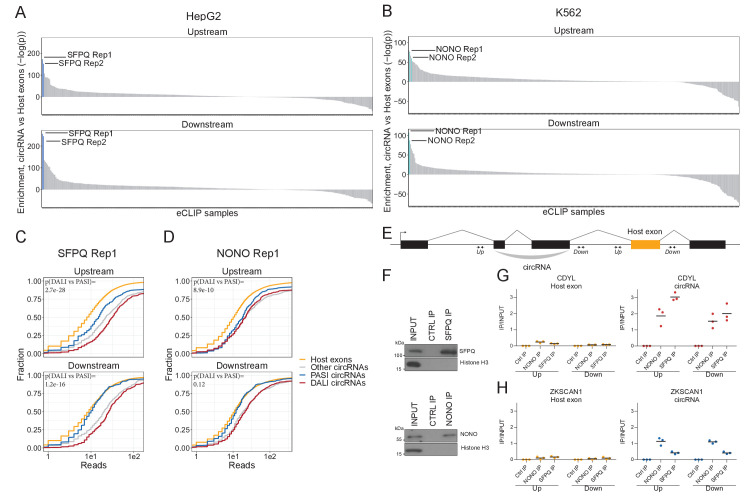
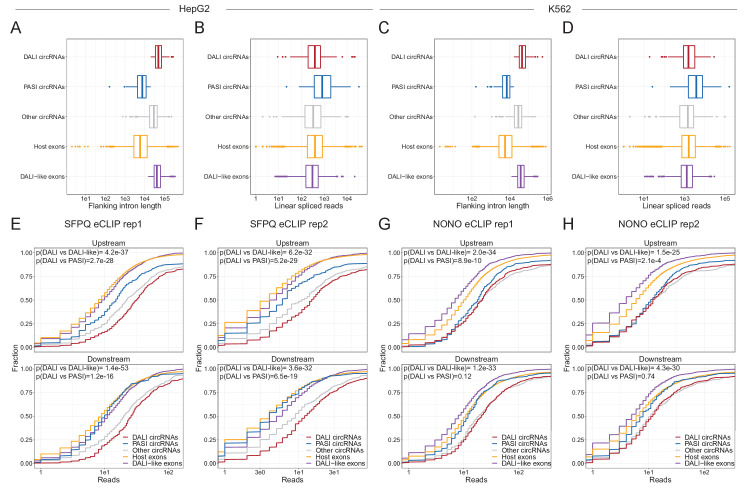
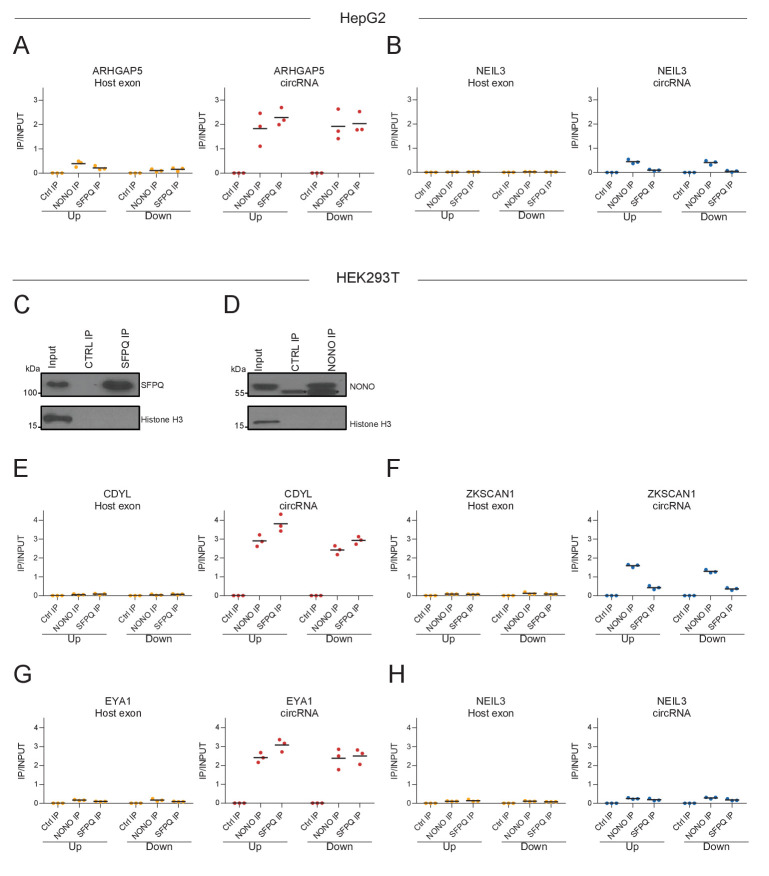
Figure 2. SFPQ and NONO show enriched binding in the flanking regions of DALI circRNAs.
(A–B) Barplot showing enrichment/depletion of eCLIP signal (see Supplementary file 2) in the vicinity of circRNAs (+/- 2000 nt) compared to host exons (+/- 2000 nt) as determined by Wilcoxon rank-sum tests for HepG2 (A) and K562 (B) eCLIP samples. (C–D) Cumulative plots of SFPQ (C) and NONO (D) eCLIP read distribution upstream and downstream of circRNA subgroups and host exons as denoted. (E) Schematic showing localization of primers (+/- 2000 nt) for targeting either upstream (up) or downstream (down) intronic regions of splice sites in respect to circRNA exons or host exon. (F) Western blotting of immunoprecipitated (IP), endogenous SFPQ or NONO from nuclear fractions of HepG2 cells with Histone H3 as a loading control. (G–H) RT-qPCR of intronic regions flanking a downstream host gene exon (left facet) or flanking the circRNA producing exon(s) (right facet) of CDYL (G) and ZKSCAN1 (H) upon RNA IP of endogenous SFPQ or NONO from nuclear fractions of HepG2 cells. The relative expression of immunoprecipitate (IP)/input is plotted. Data for three biological replicates are shown.