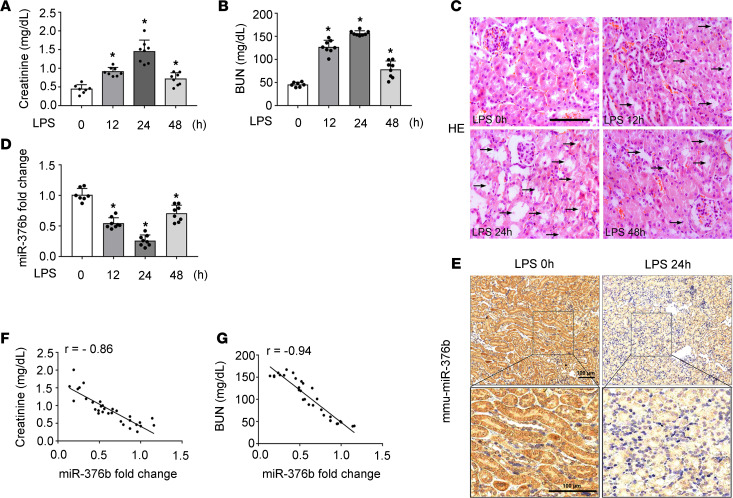
Figure 1. miR-376b is downregulated in renal tubular cells during LPS-induced endotoxic AKI.
Male C57BL/6 mice were injected with one dose of LPS (10 mg/kg) and samples were collected at indicated time points. Control mice (LPS 0h) were injected with normal saline. All quantitative data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 7 or n = 8, 2-tailed Student’s t test), *P < 0.05 vs. control. (A) Time-dependent increase of serum creatinine in LPS-treated mice. (B) Time-dependent increase of BUN in LPS-treated mice. (C) Representative images of H&E staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) qPCR analysis showing miR-376b decrease in kidneys in LPS-treated mice. The level of miR-376b was normalized to the level of sno202 (internal loading control) of the same samples to determine the ratio with the ratio of control mice arbitrarily set as 1. (E) In situ hybridization showing miR-376b decrease in kidney tissues after LPS treatment. Images on the bottom row show high-magnification views of the boxed areas in the top row. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Correlation analysis of miR-376b expression in renal tissue with serum creatinine in LPS-treated mice (r = –0.86, Spearman’s correlation test). (G) Correlation analysis of miR-376b expression in renal tissue with BUN in LPS-treated mice (r = –0.94, Spearman’s correlation test).