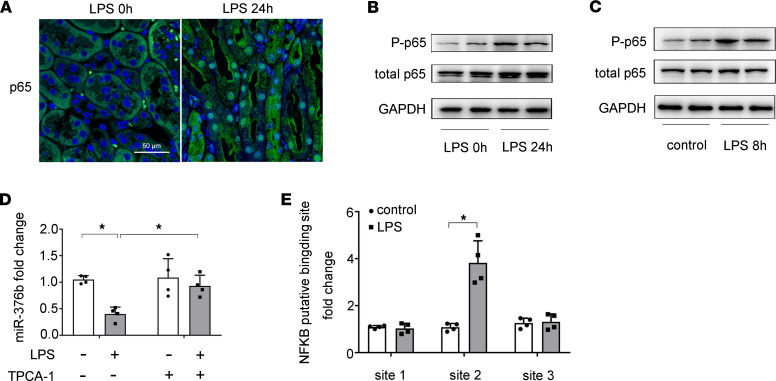
Figure 3. NF-κB mediates the downregulation of miR-376b in LPS-induced AKI.
(A) Immunofluorescence showing nuclear translocation of p65/NF-κB in renal tubule cells in LPS-treated mice. Images were collected by laser scanned confocal microscopy. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Immunoblots showing increases of p-p65 and p65 in kidney tissues of LPS-treated mice. GAPDH was used as internal control. (C) Immunoblots showing LPS-induced p-p65 and p65 in BUMPT cells. GAPDH was used as internal control. (D) qPCR analysis showing that LPS-induced decrease of miR-376b is prevented by TPCA-1. BUMPT cells were treated with 100 μM TPCA-1 and then treated with LPS. Total RNA samples were extracted after LPS treatment to quantify miR-376b by qPCR. The levels of miR-376b were normalized to the levels of sno202 of the same samples to determine the ratios. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 4, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test), *P < 0.05. (E) ChIP analysis of NF-κB binding in miR-376b promoter. BUMPT cells were treated with or without LPS for 8 hours to collect the chromatin for immunoprecipitation with a specific anti–NF-κB antibody. The immunoprecipitated samples were subjected to qPCR analysis of miR-376b promoter sequence. Quantitative data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 4, 2-tailed Student’s t test), *P < 0.05.