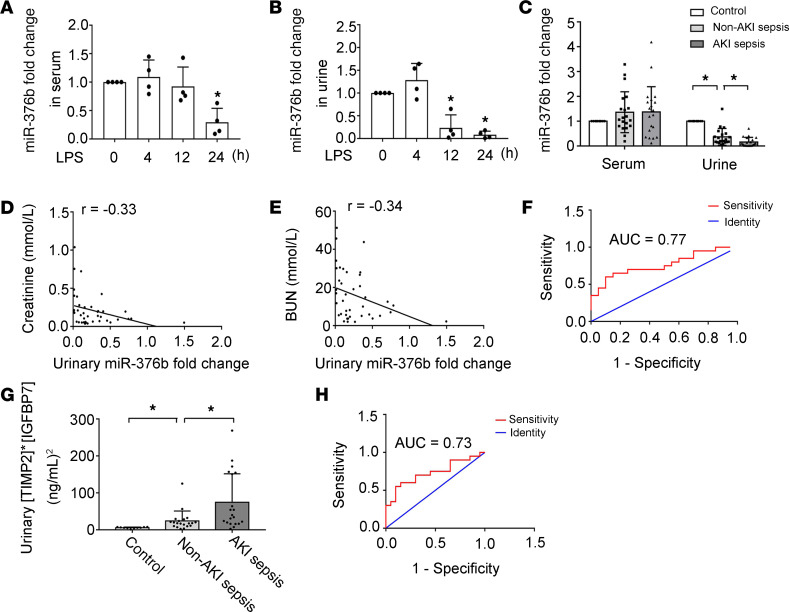
Figure 9. Evaluation of urinary miR-376b as a biomarker for septic AKI.
(A and B) Male C57BL/6 mice were injected with 10 mg/kg LPS to collect serum and urine samples at indicated time points to measure miR-376b. The values were normalized with that of control mice (LPS time 0) which was arbitrarily set as 1. Serum miR-376b showed a significant decrease at 24 hours after LPS exposure (A), whereas urinary miR-376b showed a significant decrease at 12 and 24 hours (B). All values in A and B are presented as mean ± SD (n = 4, 2-tailed Student’s t test), *P < 0.05 vs. control mice. (C) Serum and urinary miR-376b in healthy subjects (control) and patients with sepsis with or without AKI. The values were normalized with that of serum or urinary miR-376b of healthy subjects (control), which was arbitrarily set as 1. (D) Correlation analysis of urinary miR-376b with serum creatinine in patients with sepsis (r = –0.33 Spearman’s correlation test). (E) Correlation analysis of urinary miR-376b with BUN in patients with sepsis (r = –0.34, Spearman’s correlation test). (F) ROC curves for the detection of septic AKI in patients with sepsis using urinary miR-376b. (G) Urinary [TIMP2]*[IGFBP7] in healthy subjects and patients with sepsis with or without AKI. (H) ROC curves for the detection of AKI in patients with sepsis using urinary [TIMP2]*[IGFBP7]. Values in C and G are presented as mean ± SD (n = 10 or n = 20, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test), *P < 0.05.