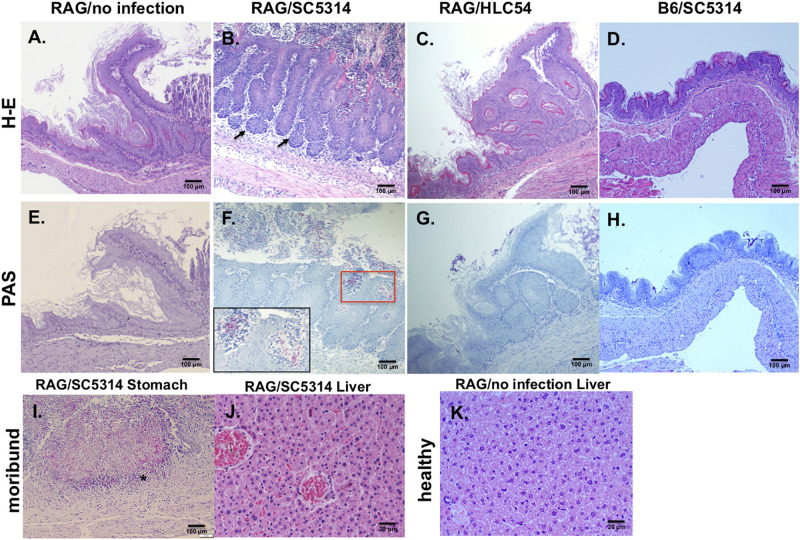
FIGURE 3.
Histological features of wild-type C. albicans caused disseminated candidiasis in Rag2γc mice. Rag2γc mice were either uninfected (A,E,K) or infected by oral gavage with 1 × 107 wild-type SC5314 (B,F,I,J) or HLC54 mutant cells (C,G). B6 mice were infected by oral gavage with 1 × 107 wild-type SC5314 cells (D,H) as controls. (A–H) Infected mice were sacrificed 12 days post infection and stomach tissues were collected and fixed for H-E (A–D) or PAS (E–H) staining. The locations in the gastric mucosa showing focal hyperplasia are marked with arrows. A magnified image of the C. albicans hyphae located in the red square is shown inside the box in the lower left corner. (I,J) The SC5314-infected Rag2γc mice were sacrificed when they became moribund (15–22 days after infection) and tissues were collected for staining. Typical images of stomach tissue stained with PAS (I) and H-E stained liver tissues from moribund mice (J) or healthy control (K) are shown. The location of hyphae penetrated into the muscular layer of the stomach is indicated with an asterisk.