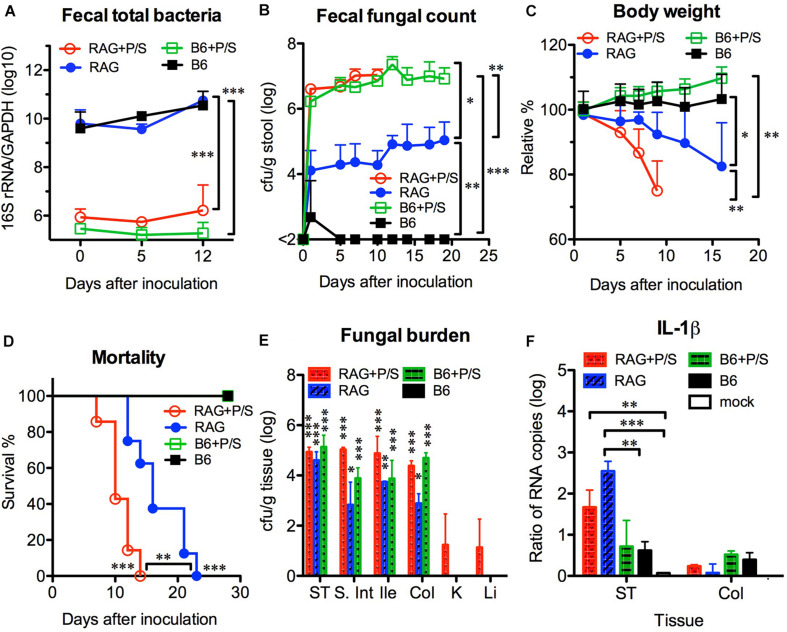
FIGURE 4.
Antibiotic treatment enhanced the severity of Candida albicans GI infection in Rag2γc mice. Groups of Rag2γc (RAG; n = 8) or B6 (n = 6) mice either treated with antibiotics (P/S) or not treated were infected with 1 × 107 C. albicans SC5314 cells by oral gavage. The abundance of total fecal bacteria was determined by qPCR of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene (A). The fecal fungal counts (B), body weight changes (C), and survival rates (D) from two independent animal experiments are combined and presented as the mean value with SD. Two mice from each group were sacrificed 14 days after infection, and the tissue fungal burden (E) and tissue level of IL-1β RNA (F) were assayed by culture and qRT-PCR, respectively. For statistical analysis, 1-way ANOVA (A–C) and the Mantel-Cox test (D) were used (*, **, and ***, for p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively).