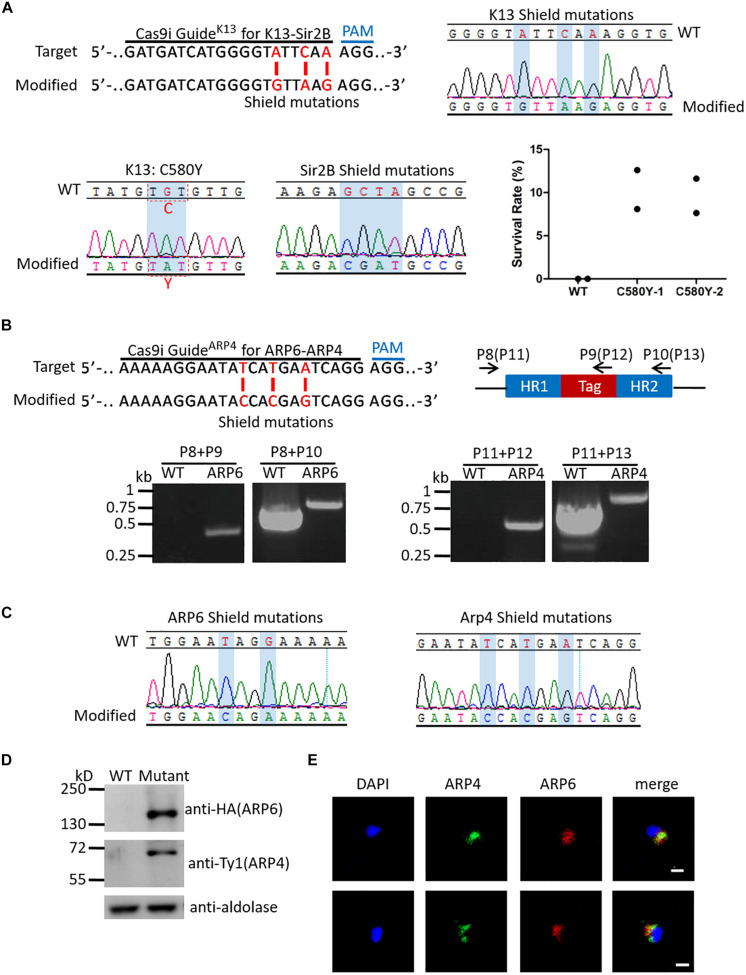
FIGURE 3.
Examination of multiplex genome editing. (A) Top left: K13 target sequence for generation of K13::Sir2B-mutCas9i highlighting the 20-nt guide sequence and the PAM (top). Modified locus shows the shield mutations (red) (bottom). Top right: DNA sequencing analysis of K13 shield mutations in K13::Sir2B-mutCas9i. Desired shield mutations are highlighted. Bottom left: DNA sequencing analysis of K13_C580Y mutation in K13::Sir2B-mutCas9i. C580Y mutation is highlighted. Bottom middle: DNA sequencing analysis of Sir2B shield mutations in K13::Sir2B-mutCas9i. Desired shield mutations are highlighted. The 20-bp target and shield mutations for Sir2B are the same as those used in single gene editing. Bottom right: Survival rates of RSA0– 3 h for K13::Sir2B-mutCas9i clones and WT. Survival rates of mutant clones (mean 10.36, 9.62%) are significantly higher than WT (none), confirming the correlation between K13_C580Y mutation and artemisinin resistance. n = 2. WT, wild-type 3D7. (B) Top left: ARP4 target sequence for generation of ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i highlighting the 20-nt guide sequence and the PAM (top). Modified locus shows the shield mutations (red) (bottom). The 20-bp target and shield mutations for APP6 are the same as those used in single gene editing. Top right: Diagram illustrating the primers used for PCR verification of ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i. Primers for ARP6 (primers P8, P9, and P10) and ARP4 (primers P11, P12, and P13; in brackets) are indicated respectively. Bottom: PCR analysis of ARP6 (left) and ARP4 (right) in ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i and WT. The result confirms the presence of HA tag in ARP6 (primers P8/P9, 446 bp in the mutant; primers P8/P10, 740 bp in the WT and 800 bp in the mutant) and Ty1 tag in ARP4 (primers P11/P12, 502 bp in the mutant; primers P11/P13, 738 bp in the WT and 810 bp in the mutant). (C) DNA sequencing analysis of shield mutations in ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i. Desired shield mutations of ARP6 (left) and ARP4 (right) are highlighted. (D) Western blotting of ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i and WT. We used the mouse anti-HA antibody to check the ∼116 kDa ARP6-HA protein and mouse anti-Ty1 antibody to check the ∼60 kDa ARP4-Ty1 protein. The result shows the expression of ARP6-HA and Arp4-Ty1 proteins. Mutant, ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i. (E) IFA analysis of ARP6-HA::ARP4-Ty1Cas9i. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue fluorescence). The green fluorescence represents ARP4-Ty1 and the red fluorescence represents ARP6-HA. IFA reveals the co-localization of ARP4 and ARP6 in the nucleus. Bar = 5 μm.