Fig. 1.
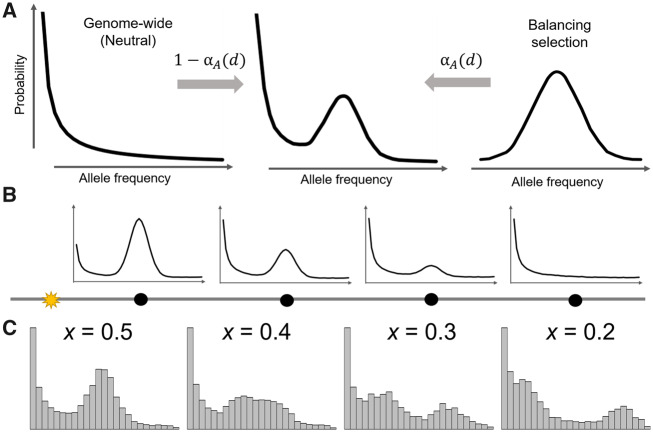
Schematic of the mixture model underlying the B statistics. (A) The model for the alternative hypothesis is a mixture of the distribution of allele frequencies under balancing selection at proportion , modeled by a binomial distribution, and the distribution under neutrality at proportion , modeled by the genome-wide SFS. Here, decays as a function of recombination distance d, and so sites close to (i.e., small d) the putative selected site will be modeled mostly by the distribution expected under balancing selection, whereas sites far from (i.e., large d) the selected site will be modeled mostly by the distribution expected under neutrality. (B) Distributions of allele frequencies at neutral sites (black dots) under the mixture model at varying distances d from the putative selected site (yellow star). (C) Distributions of allele frequencies from the center 10 kb (0.01 cM) of the simulated sequences when balancing selection maintains the equilibrium frequency of x = 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, or 0.5.