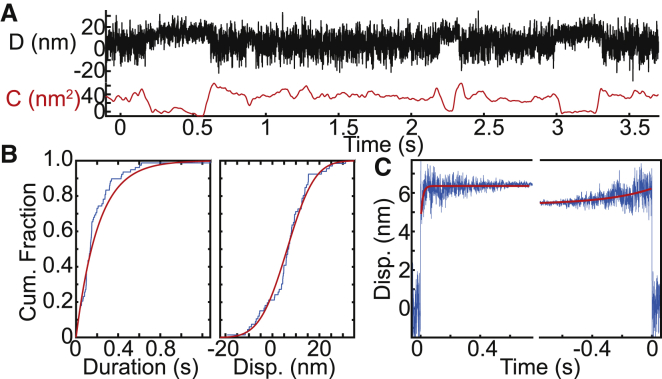
Figure 6.
Ensemble averages of experimental optical trapping data. The kinetics and mechanics of cardiac myosin in 1 μM ATP were measured using the three-bead assay. (A) Experimental data trace shows the displacement (D) and covariance (C). (B) Cumulative distributions for the (left) binding interaction durations and (right) total working stroke displacements are shown. The peak-to-peak method was used to detect binding interactions. Red lines show the cumulative fits based on (left) exponential and (right) normal distributions. The characteristic rate obtained from the fit to the distribution of attachment durations gives a detachment rate equal to 4.7 s−1, which is consistent with the expected rate of ATP-induced actomyosin dissociation at 1 μM ATP. The distribution of total step sizes has a mean of 6.3 nm and a standard deviation of 9.2 nm. (C) The change-point algorithm was used to align the interactions identified using the peak-to-peak method. A total of 66 binding interactions from five molecules were analyzed. The resulting ensemble averages have estimated substep sizes of 4.4 and 2.0 nm. The estimated time-forward rate is 74 s−1, and the estimated time-reversed rate is 3.2 s−1. These values are consistent with previous measurements using a much larger data set, and they agree well with the previously measured rates of ADP release and ATP-induced dissociation 1 μM ATP. To see this figure in color, go online.