Figure 5.
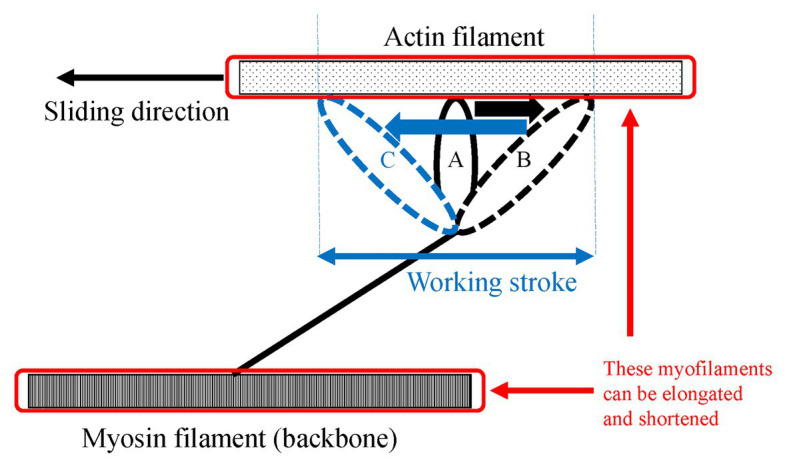
Schematic explanation of the shortening of sarcomere after an active stretch. Due to an active stretch, attached cross-bridges are elongated from the position A to the position B. Then, the elongated attached cross-bridges moves from the position B to the position C during the subsequent active shortening. This movement is called the working stroke. In addition to this deformation of the attached cross-bridges, myosin, and action filaments can be elongated and shortened because these filaments also have compliance. Therefore, the shortening/lengthening of sarcomere is composed of not only attached cross-bridges but also the myofilaments.
