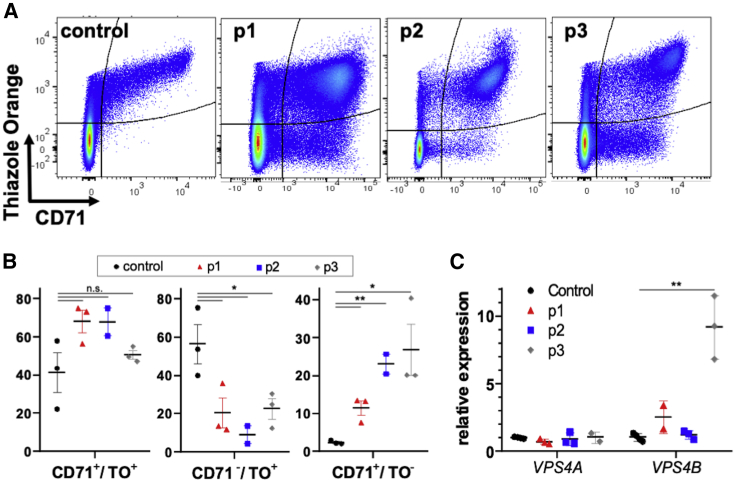
Figure 2.
Peripheral Blood Phenotype of Probands with VPS4A Mutations
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of probands’ peripheral RBCs (CD45−) showing presence of an unusual population positive for transferrin receptor (CD71+) and negative for RNA, as labeled by thiazole orange (TO).
(B) Quantification of immature RBC populations analyzed by flow cytometry and IFC (CD71+/TO+, CD71−/TO+, and CD71+/TO−) as a percentage of total CD71+ and/or TO+ cells (excluding all mature CD71−/TO− RBCs since probands 1 and 2 are regularly transfused). Samples from individuals with sickle cell disease (SCD) were used as positive controls with increased reticulocyte counts. Data shown are mean ± SEM of n = 3 experiments for all but p2 (n = 2). ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 by a Student’s t test for samples with unequal variance.
(C) Relative expression of VPS4A and VPS4B in CD71+ reticulocytes isolated from whole blood and evaluated by qPCR. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 4 control; n = 3 p1&2 VPS4A, p2&3 VPS4B; n = 2 p1 VPS4B, p3 VPS4A, ∗∗p < 0.01 by a Student’s t test for samples with unequal variance.