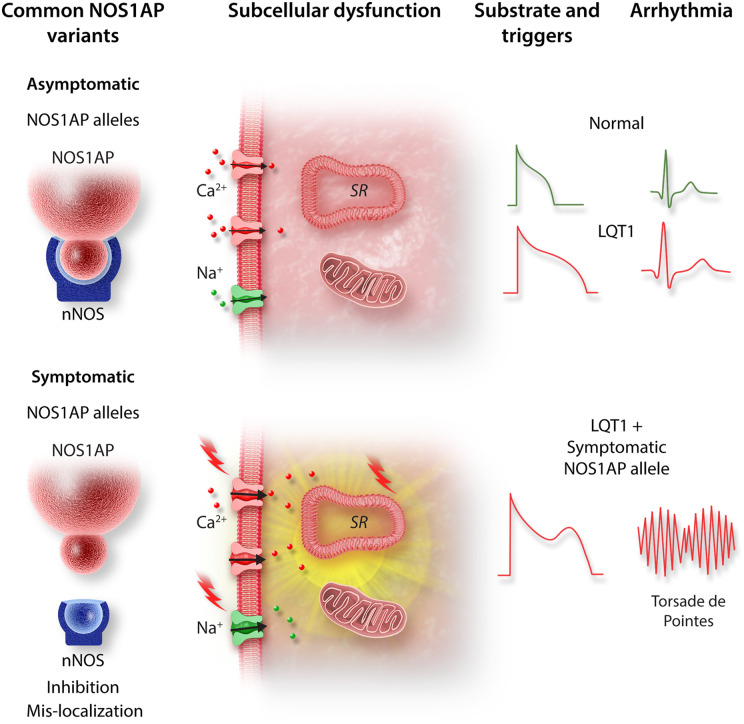
Figure 1.
Schematic illustrating the proposed mechanism by which a minor NOS1AP allele unmasks the arrhythmogenic nature of a LQT1-causing KCNQ1 mutation. The minor NOS1AP variant exhibits reduced co-localization with its primary cellular target nNOS resulting in loss of nNOS function. This causes aberrant nNOS/NO signalling at key cellular compartments, thereby causing action potential prolongation and destabilization of intracellular calcium cycling. Combined, these loss of nNOS function effects form the triggers and substrate required for torsade de pointes.