Table 1.
Gene set analysis methods under benchmark
| Method | Author | Year |
Citations

|
RNA-seq |
Gene statistic
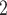
|
Set statistic | Significance estimation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORA | –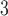
|
–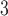
|
–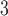
|
✓ | user-defined | DE / GS overlap | Fisher’s exact test |
| GLOBALTEST | Goeman et al. [68] | 2004 | 983 | – | – |
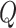 statistic statistic |
Empirical Bayes GLM |
| GSEA | Subramanian et al. [7] | 2005 | 16 730 | – |
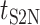
|
KS statistic | Sample permutation |
| SAFE | Barry et al. [54] | 2005 | 350 | – | Student’s 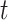
|
Wilcoxon rank sum | Sample permutation |
| GSA | Efron and Tibshirani [62] | 2007 | 798 | – |
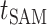
|
Maxmean | Sample permutation |
| SAMGS | Dinu et al. [69] | 2007 | 270 | – |
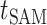
|
Hotelling’s 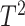
|
Sample permutation |
| ROAST | Wu et al. [70] | 2010 | 253 | ✓ |
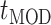
|
Weighted mean | Rotation |
| CAMERA | Wu and Smyth [66] | 2012 | 246 | ✓ |
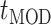
|
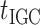
|
Two-sample 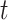 -test -test |
| PADOG | Tarca et al. [25] | 2012 | 71 | – |
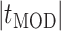
|
Weighted mean | Sample permutation |
| GSVA | Hänzelmann et al. [71] | 2013 | 471 | ✓ | – | KS statistic | Empirical Bayes GLM |
See Supplementary Table S3 for additional methodological differences including directionality, supported experimental designs and whether a pre-ranked execution mode is available. Abbreviations: DE, differential expression; GS, gene set; KS, Kolmogorov–Smirnov; GLM, generalized linear model.1Google Scholar, May 2019.2Notation for specific modifications of the regular 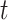 -statistic:
-statistic: 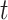 -like signal-to-noise ratio
-like signal-to-noise ratio 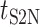 [59]; SAM’s
[59]; SAM’s 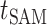 accounting for small variability at low expression levels [72]; moderated
accounting for small variability at low expression levels [72]; moderated 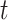 -statistic
-statistic 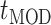 [38]; and extended
[38]; and extended 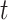 -statistic accounting for inter-gene correlation
-statistic accounting for inter-gene correlation 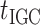 [66].3Popular implementations are available in DAVID [8] and PathwayStudio [67] among many others [11].
[66].3Popular implementations are available in DAVID [8] and PathwayStudio [67] among many others [11].
