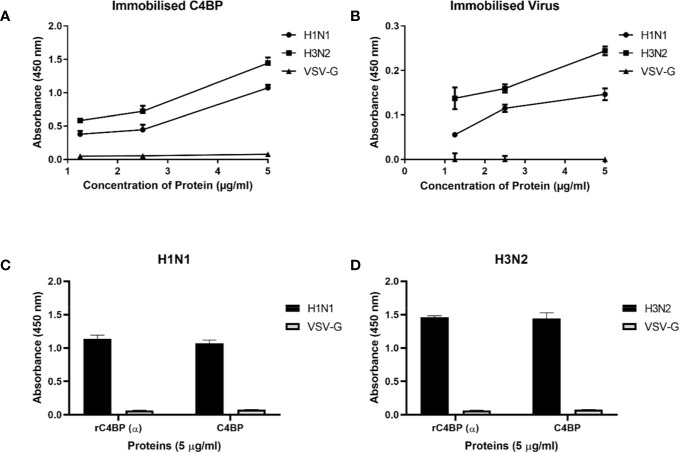
Figure 2.
Binding interaction of immobilized C4BP to IAV subtypes (A), and immobilized IAV subtypes to C4BP (B). Microtiter wells were coated with a varied concentration of C4BP (5, 2.5, and 1.25 µg/ml) protein and incubated with constant volume of viruses (1,000 PFU/ml). Bound C4BP-IAV was probed with monoclonal anti-influenza virus H1 and polyclonal anti-influenza virus H3 antibody (1:5,000). Another ELISA was performed by coating a constant concentration of IAV subtypes (1,000 PFU/ml) and incubated with a varied concentration of C4BP protein (5, 2.5, and 1.25 µg/ml). IAV-C4BP interaction was detected using polyclonal rabbit anti-human C4BP antibodies and anti-rabbit IgG-HRP-conjugated antibody (1:5,000). A validation ELISA to show the detection of H1N1 (C) and H3N2 (D) binding to a recombinant C4BP (rC4BP) and plasma purified C4BP. Microtiter wells were coated with immobilized rC4BP and the plasma purified C4BP (5 µg/ml), and incubated with H1N1 or H3N2 (1,000 PFU/ml). The binding between immobilized proteins and IAV subtypes were detected using monoclonal anti-influenza virus H1 and polyclonal anti-influenza virus H3 antibody (1:5,000). VSV-G pseudo-typed lentiviral particles were used as a negative control; no significant binding was observed. The data were expressed as the mean of three independent experiments done in triplicates ± SEM.