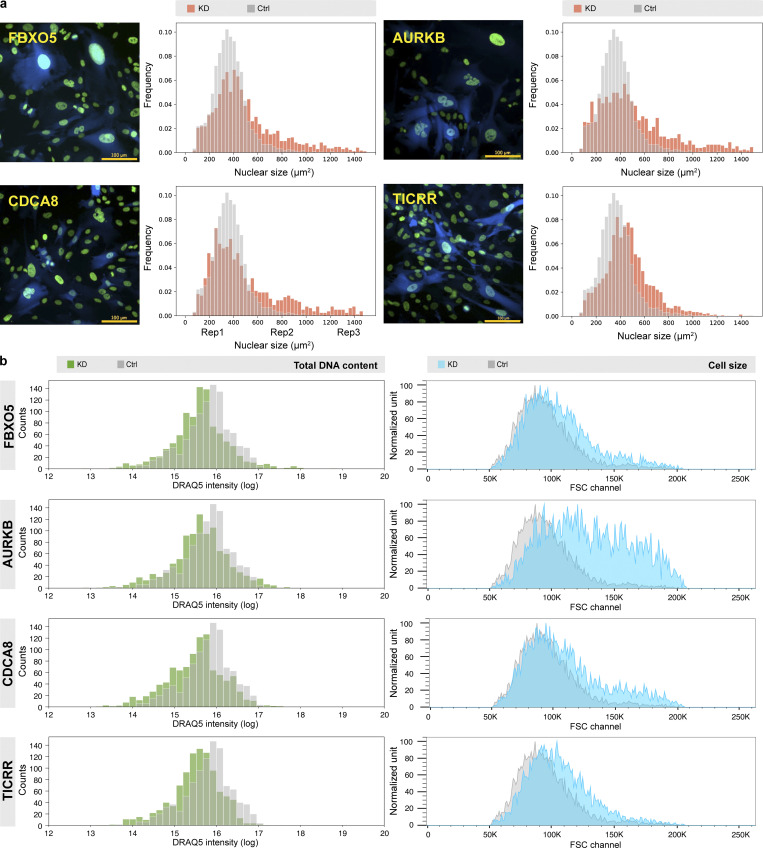
Figure 5.
Characterization of hits identified in nuclear size screen. (a) Each hit identified in both replicates was verified under the microscope after infecting with a mixture of three to four sgRNA constructs targeting the gene (n = 3). Cells were puromycin selected for 2 d before imaging. Example images of four hits and their distribution of nuclear sizes from one replicate are shown in panel a; all the others are listed in Fig. S6. For each gene in each replicate, at least 1,000 cells were analyzed using the Auto-PhotoConverter μManager plugin. The cell population is heterogeneous due to inefficient knockdown, incomplete puromycin selection, and penetrance of the phenotype. A BFP was expressed from the same sgRNA construct. Only cells with high BFP intensity, indicating successful sgRNA transduction, were included for data analysis as described in Materials and methods. Red, nuclear size distribution of corresponding gene after knockdown; gray, nuclear size distribution of cells infected with nontargeting control sgRNAs. (b) Some cells developed a larger cellular size while maintaining a similar DNA content level after knockdown. For DNA content measurement, cells were infected with the same three to four sgRNAs/gene, puromycin selected for 2 d, and stained with 5 µM DRAQ5 for 1 h before imaging (1,000 cells were analyzed for each gene). For cellular size measurement, cells were infected with the same three to four sgRNAs/gene and puromycin selected for 3 d before FACS analysis (at least 2,787 cells were analyzed for each gene). Example imaging analysis data and FACS data of the same four hits are shown in b, and all the others are shown in Fig. S6. Green, distribution analysis of DRAQ5 staining intensity after knockdown of corresponding gene; blue, FACS of FSC signal after knockdown of corresponding gene; gray, distribution analysis of DRAQ5 staining intensity or FSC signal of cells infected with nontargeting control sgRNAs.