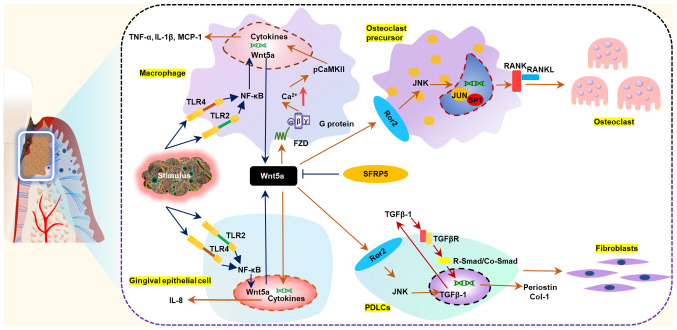
Figure 2.
Wnt5a participates in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and regulates periodontal non-mineralized homeostasis and bone homeostasis. Under physiological conditions, Wnt5a contributes to maintaining a non-mineralized state of periodontal ligament and regulating bone homeostasis by promoting fibrillogenesis of periodontal ligament cells and osteoclastogenesis of osteoclast precursors. During the occurrence and development of periodontitis, Wnt5a expression levels increase in response to pathogen stimulation. Excessive production of Wnt5a amplifies the inflammatory response and accelerates the destruction of periodontal tissues. Sfrp5 antagonizes the proinflammatory effects of Wnt5a. CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II; Col-1, collagen 1; FZD, frizzled; MCP-1, monocyte chemotactic protein 1; PDLC, periodontal ligament cell; RANK, receptor activator of NF-κB; RANKL, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand; Ror2, receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2; Sfrp5, secreted frizzled-related protein 5; TLR, toll-like receptor; Wnt5a, Wnt family member 5a.