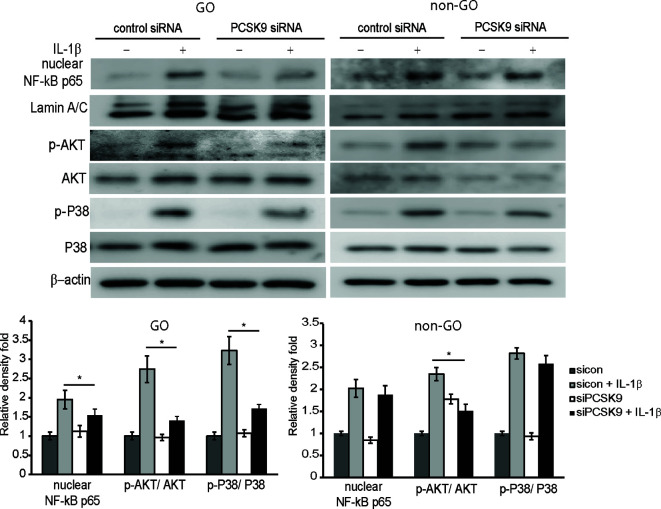
Figure 4.
Effect of silencing proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) on the activation of signal molecules by interleukin-1β (IL-1β) treatment. Confluent orbital fibroblasts obtained from Graves’ orbitopathy (GO) patients (n=3) were treated with or without 10 ng/ml of IL-1β after transfection with control siRNA or PCSK9 siRNA (50 nM, 24 h). Treatment with IL-1β (10 ng/ml, 60 min) resulted in an increase in the levels of nuclear NF-κB p65 and phosphorylated forms of Akt and p38. The treatment with PCSK9 siRNA in GO cells significantly blunted the increases in the transcription factors. However, in fibroblasts from non-GO subjects (n=3), the PCSK9 inhibition only suppressed the phosphorylated Akt. Representative gel images are shown. Data in the columns indicate the mean density ratio ± SD of the bands obtained from the GO patients, normalized to the level of β-actin in the same sample (*p < 0.05 between sicon + IL-1β and siPCSK9 + IL-1β).