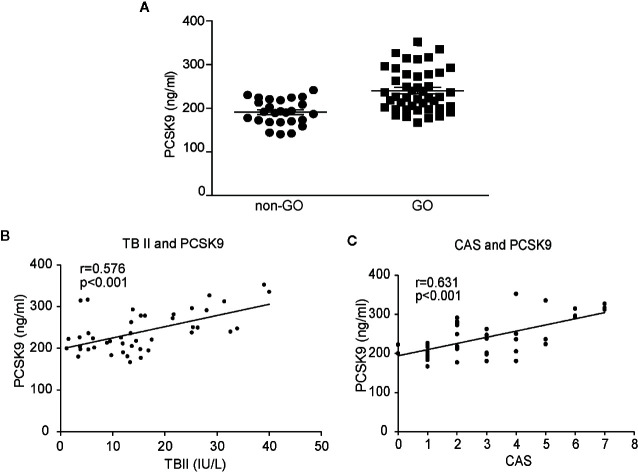
Figure 6.
Comparison of plasma levels of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) between Graves’ orbitopathy (GO) patients and non-GO subjects, and correlation analyses between plasma levels of PCSK9, thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin and clinical activity score (CAS). The plasma levels of PCSK9 were measured in GO patients and non-GO subjects using ELISA. The samples were assayed in triplicate. (A) The mean PCSK9 plasma level was significantly higher in the GO patients (n=44, 239.97 ± 48.20 ng/ml) than the healthy subjects (n=26, 190.83 ± 28.77 ng/ml; p < 0.01). A single dot represents the value obtained from a single donor. The results of Spearman’s rank correlation test between plasma levels of PCSK9 (GO patients, n=44) and (B) plasma levels of thyrotropin binding inhibitory immunoglobulin (TBII) (GO patients, n=44) or (C) clinical activity score (CAS) (GO patients, n=44) are shown. The plasma PCSK9 concentrations showed significant associations with the plasma TBII levels (r = 0.576, p < 0.001) and CAS (r = 0.631, p < 0.001).