Table 1.
Definitions, examples, and chemical structures of bio‐based, biodegradable, and oxo‐ and hydro‐degradable plastics.
|
Plastic |
Definition |
Example[a] |
Chemical structure |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
bio‐based |
a plastic made from renewable resources, namely biomass or waste |
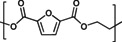
PEF |
|
[31] |
|
bio‐degradable |
a plastic that can be assimilated by bacteria and/or fungi to give environmentally friendly products |
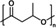
PHB (bio‐based) |
|
[30] |
|
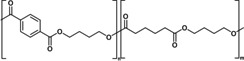
PBAT (fossil‐carbon‐based) |
|
[30] |
||
|
oxo‐degradable |
a plastic whose degradability is induced by additives that initiate oxidation reactions |
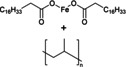
Oxo‐PP |
|
[20, 21] |
|
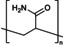
hydro‐degradable |
a plastic whose degradability is induced by the polar groups susceptible to hydrolysis |
PA |
|
[24–27] |
[a] PEF=polyethylene furanoate; PHB=poly‐4‐hydroxybutyrate; PBAT=polybutylene adipate terephthalate; Oxo‐PP=oxo‐degradable polypropylene; PA=polyacrylamide.