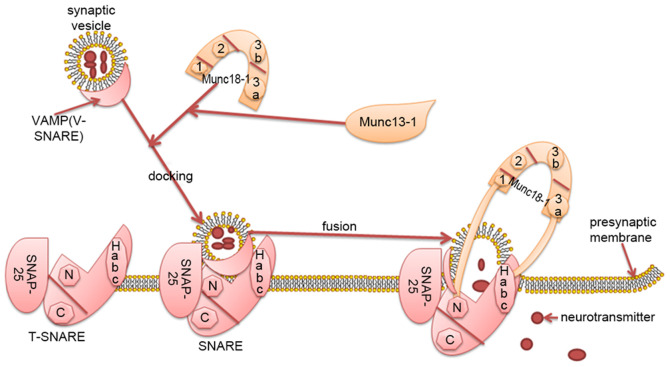
Figure 1.
Munc18-1regulates neurotransmitter transmission by interacting with the SNARE complex. The SNARE protein is mainly composed of SNAP-25, vesicular-associated membrane protein and syntaxin1. SNAP-25 and syntaxin1 form the target membrane of vesicle protein (T-SNARE), which binds to synaptic vesicle protein (VAMP). Munc18-1 has a complex, arched, tertiary structure. The arch consists of four closely connected domains named 1, 2, 3a and 3b. Domain 1 and 3a form an arched gap. Syntaxin-1 is the core protein of SNARE. Munc18-1 primarily regulates vesicle fusion by interacting with syntaxin-1 (Habc domain; N-terminal short peptide). Domain 3a is in close contact with the Habc domain of syntaxin-1, domain 1 is located on the other side of the arched gap and binds to the N-terminal short peptide of syntaxin-1. Munc13-1 bridges synaptic vesicles and presynaptic membrane fusion to coordinate the assembly of SNARE with Munc18-1. Munc18-1 regulates vesicle docking and fusion by interacting with the SNARE complex, affects the released vesicles and participates in the transmission of neurotransmitters. Munc, mammalian uncoordinated; SNARE, soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; SNAP25, synaptosomal-associated protein of 25 kDa; T-SNARE, target membrane of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; V-SNARE, synaptic vesicle protein of soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor; VAMP, vesicular-associated membrane protein; N, N-terminus; C, C-terminus; 1, domain 2; 2, domain 2; 3a; domain 3a; 3b, domain 3b.