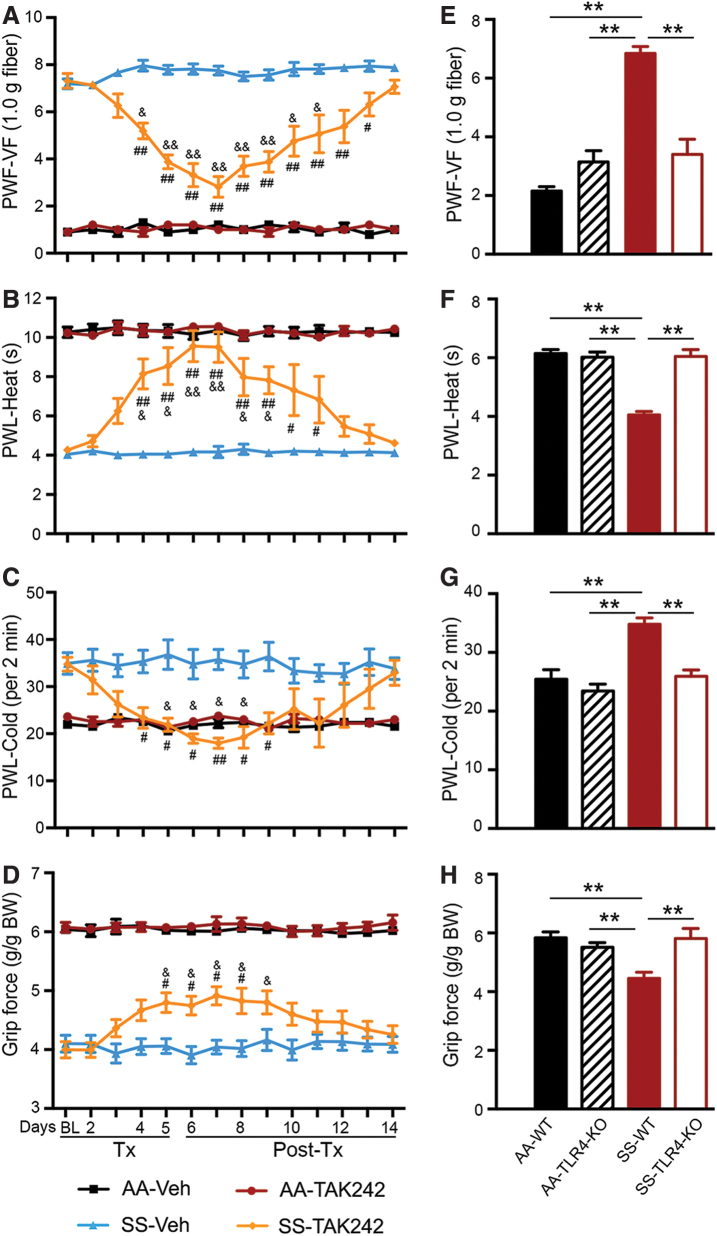
FIG. 2.
TLR4 inhibition (TAK242) and TLR4 deletion reduces hyperalgesia in sickle mice. Mice (A–D) received TAK242 (1 mg/kg/day, i.v.) or Veh for 5 days. Pain testing was performed before any treatment (BL), 20 h after each injection during treatment, and daily after TAK242 treatment for 9 days (Supplementary Fig. S5B). (E–H) Pain performance was measured in HbSS-BERK without TLR4 (SS-TLR4-KO), HbAA-BERK without TLR4 (AA-TLR4-KO), receptor WT HbSS-BERK sickle mice, and HbAA-BERK control mice. (A, E) Mechanical hyperalgesia. (B, F) Heat sensitivity. (C, G) Cold sensitivity. (D, H). Deep tissue/musculoskeletal hyperalgesia. Mean age of each group in months ± SEM: (A–D) HbAA-BERK: 6.04 ± 0.18 (Veh, n = 6); 5.92 ± 0.33 (TAK242, n = 6) and HbSS-BERK: 6.07 ± 0.05 (Veh, n = 8); 6.00 ± 0.33 (TAK242, n = 8). (E–H) HbAA-BERK (5.92 ± 0.72, n = 8); HbSS-BERK (6.00 ± 0.88, n = 8); AA-TLR4-KO (5.88 ± 0.96, n = 8); SS-TLR4-KO (6.02 ± 0.89, n = 5). (A–D) HbAA-BERK: 6.04 ± 0.18; Veh n = 6, TAK242 n = 6; HbSS-BERK: 6.0 ± 0.33; Veh, n = 8, TAK242 n = 8). (E–H) HbAA-BERK: 5.9 ± 0.7 (n = 8); HbSS-BERK: 6.0 ± 0.9 (n = 8); AA-TLR4-KO: 5.9 ± 1.0 (n = 8); and SS-TLR4-KO: 6.0 ± 0.9 (n = 5). All data are mean ± SEM. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.001 in HbSS-BERK for treatment versus corresponding vehicle at each time-point (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). &p < 0.05, &&p < 0.001 in HbSS-BERK for each time-point versus BL in each treatment group (one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). **p < 0.001 (Student's unpaired t test). AA: HbAA-BERK; AA-TLR4-KO: TLR4 knockout HbAA-BERK; SS: HbSS-BERK; SS-TLR4-KO: TLR4 knockout HbSS-BERK; WT: TLR4 wild type. i.v., intravenous; TAK242, resatorvid; selective small molecule inhibitor of TLR4; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TLR4-KO, TLR4 knockout (genetic deletion); WT, wild type. Color images are available online.