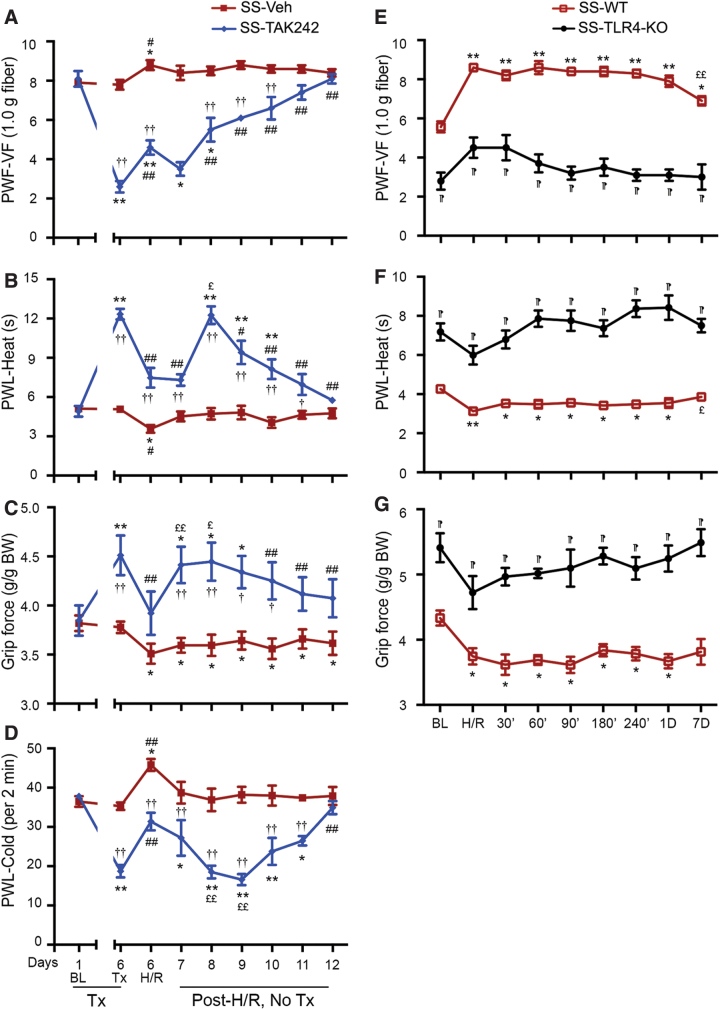
FIG. 3.
TLR4 mediates H/R-induced acute pain in sickle mice. (A–D) HbSS-BERK (SS) mice received intralipid Veh or TAK242 (1 mg/kg/day, i.v.) for 5 days. Twenty-four hours after the last injection, mice were subjected to H/R treatment. Pain testing was performed before any treatment (BL), under normoxia before H/R (Tx, pre-H/R), immediately after H/R (H/R), and daily post-H/R (Supplementary Fig. S5C). (E–G) SS-TLR4-KO and age-matched TLR4 WT HbSS-BERK (SS-WT) sickle mice were subjected to H/R treatment. Pain behaviors were assessed under normoxia before H/R (BL), immediately after H/R (H/R), and at the indicated time-points. (A, E) Mechanical hyperalgesia. (B, F) Heat sensitivity. (C) Cold sensitivity. (D, G) Deep tissue hyperalgesia. Mean age of each group in months ± SEM. (A–D) 7.51 ± 0.04 (n = 5) for SS-Veh and 7.39 ± 0.07 (n = 5) for SS-TAK242. (E–G) 6.25 ± 1.02 (n = 5) for SS-WT and 5.92 ± 0.93 (n = 5) for SS-TLR4-KO. Each value is the mean ± SEM. †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01 for TAK242 versus corresponding vehicle at each time-point (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus BL of corresponding group (one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus day 6 before H/R of corresponding group (one-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). £p < 0.05, ££p < 0.01 versus day 6 post H/R of corresponding group. ¶p < 0.001 for SS-TLR4-KO versus SS-WT at the respective time-point (two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni). TLR4-KO-SS, TLR4 knockout HbSS-BERK. H/R, hypoxia/reoxygenation. Color images are available online.