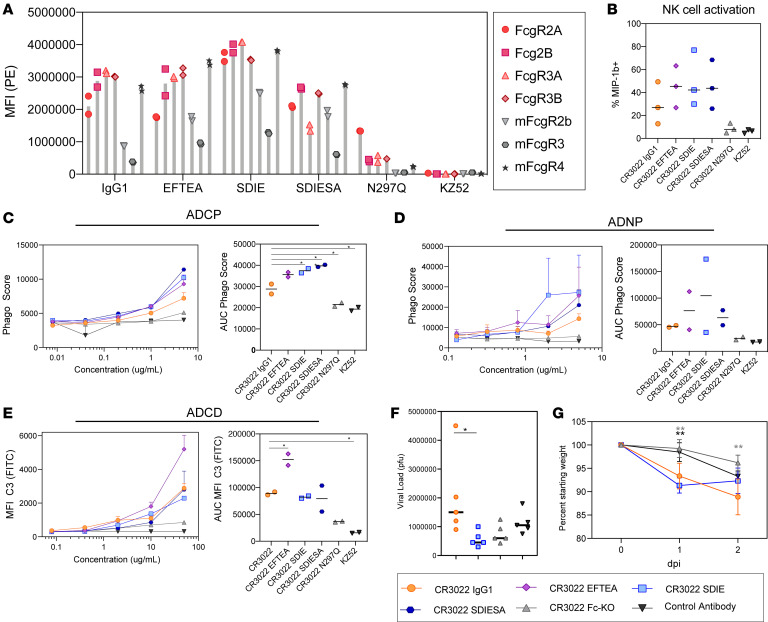
Figure 3. CR3022 can be enhanced through Fc engineering.
(A) Each CR3022 variant was analyzed for its ability to bind the human FcγR2a, FcγR2b, FcγR3a, and FcγR3b or the mouse FcγR2b, FcγR3, and FcγR4 by Luminex. Each bar represents the average MFI and error bars show standard deviation. (B) The CR3022 variants were analyzed for their ability to drive NK activation, as measured by MIP-1b activity. The bar graphs represent the average of 3 donors, and the error bars represent the standard deviation. For AUC, significance was determined by an ordinary 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05. (C–E) The CR3022 variants were evaluated for their ADCP (C), ADNP (D), and ADCD (E) activity. The dots on the line graph represent the average of 2 replicates. The bar graphs represent the average AUC of 8 serial dilutions run as replicates, and the error bars represent the standard deviation. For AUC, significance was determined by an ordinary 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05. (F and G) BALB/c mice (5 per group) were treated with a CR3022 variant or control therapeutically. Lung viral titers were determined 2 days postinfection (dpi) (F), and weight was monitored daily (G). For viral titer (F), significance was determined by an ordinary 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05. For weight (G), significance was determined by an ordinary 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, between the respective antibody, indicated by the color of the asterisk, and the CR3022 WT. For weight (G), each dot represents a mouse, and the error bars represent the standard deviation.