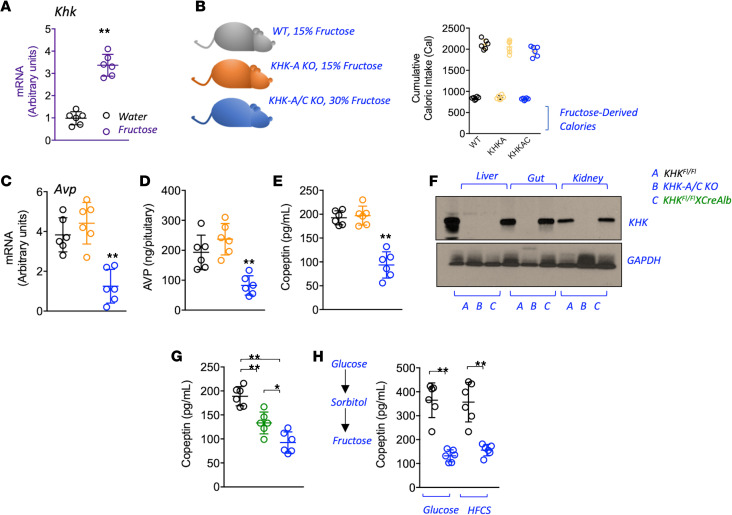
Figure 2. Fructose metabolism via fructokinase is necessary for vasopressin production and secretion.
(A) Hypothalamic mRNA levels of fructokinase (KHK) in mice receiving water or a 10% fructose solution for 30 weeks. (B) Cumulative total and fructose-derived caloric intake in WT (black), KHK-A–KO (orange), and KHK-A/C–KO (blue) mice receiving equal amounts of fructose for 30 weeks. (C) Hypothalamic mRNA levels of vasopressin in WT, KHK-A–KO, and KHK-A/C–KO mice receiving equal amounts of fructose for 30 weeks. (D) Vasopressin levels in pituitary of WT, KHK-A–KO, and KHK-A/C–KO mice receiving equal amounts of fructose for 30 weeks. (E) Serum copeptin levels in WT, KHK-A–KO, and KHK-A/C–KO mice receiving equal amounts of fructose for 30 weeks. (F) Representative Western blot (n = 3 total blots) for KHK and actin in liver, gut, and kidney tissues from WT (black), KHK-A/C–KO (blue), and liver-specific KHK-A/C–KO mice (KHKFl/FlXCreAlb, green). (G) Serum copeptin levels in WT, KHK-A/C–KO, and liver-specific KHK-A/C–KO mice receiving equal amounts of fructose for 30 weeks. (H) Serum copeptin levels in WT and KHK-A/C–KO mice receiving glucose (10%) or HFCS (10%) solutions for 30 weeks. The data in A–E and G and H are presented as the mean ± SD and analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. n = 6 mice per group. See also Supplemental Table 1 and Supplemental Table 2. KHK, ketohexokinase; KHK-A, A isoform of KHK; KHK-A/C, both A and C isoforms of KHK; HFCS, high-fructose corn syrup.