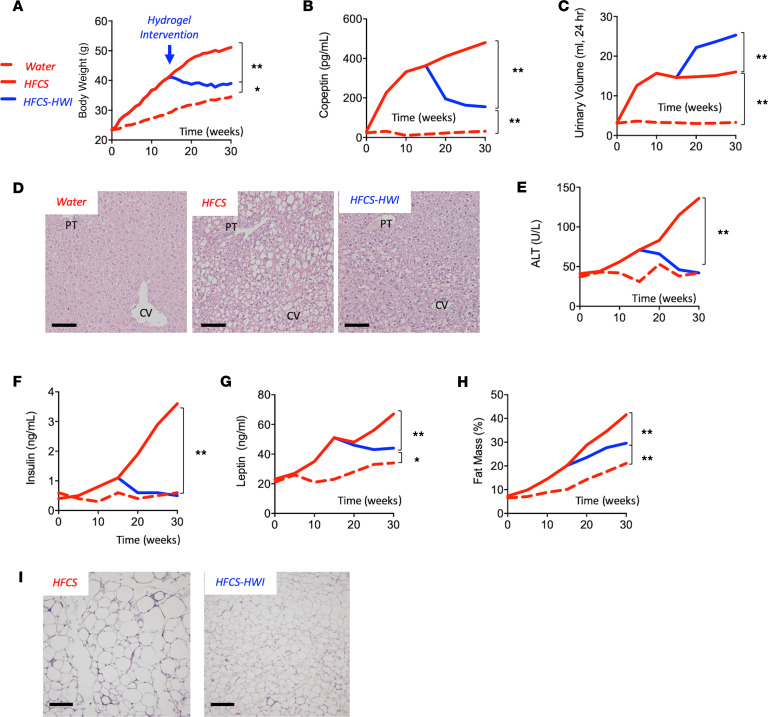
Figure 4. Lowering vasopressin as a therapeutic intervention in mice with sugar-induced metabolic syndrome.
(A) Weekly body weight gain in mice receiving water (red-dashed line) or HFCS (red solid line) for 30 weeks. At week 15 a subgroup of HFCS started the intervention with hydrogels (HFCS-HWI, blue solid line). (B) 30-week serum copeptin levels in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (C) 30-week urinary volume excretion (mL urine/24 hour) in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (D) Representative H&E images from livers of mice (n > 10 images per animal) of the same groups as in A at 30 weeks. Size bars: 50 μM. (E) 30-week serum ALT levels in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (F) 30-week serum Insulin levels in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (G) 30-week serum leptin levels in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (H) 30-week fat mass to total body weight percentage in water, HFCS, and HFCS-HWI groups. (I) Representative H&E images from epididymal adipose tissue of mice (n > 10 images per animal) on HFCS or HFCS-HWI groups. Size bars: 50 μM. The data in A–C and E–H are presented as the mean and analyzed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc. The data for A were collected and analyzed weekly, whereas the data for B and C and E–H were collected and analyzed every 5 weeks. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. n = 6 mice per group. See also Supplemental Figure 1 and Supplemental Table 4. HFCS, high-fructose corn syrup; HWI, high water intake; PT, portal triad; CV, central vein; ALT, alanine aminotransferase.