Figure 4.
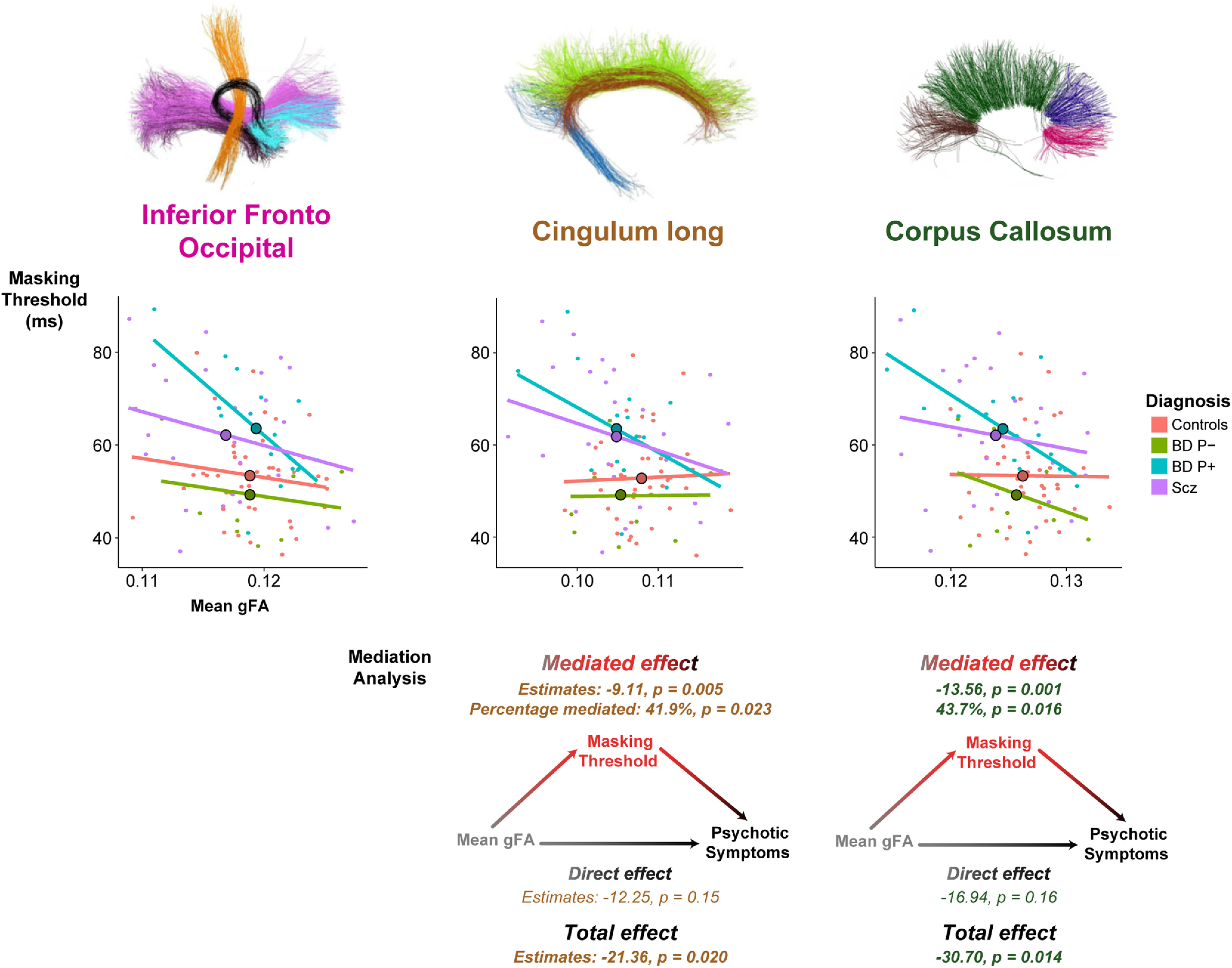
Correlation between masking threshold and the mean of gFA and mediation analysis for the three bundles of interest. Top, Masking threshold is negatively correlated with mean gFA across subjects for the inferior frontal-occipital fasciculus, the cingulum, and the corpus callosum, suggesting that conscious access relies on structural cerebral connectivity of these bundles. The masking threshold is represented as a function of the mean of gFA in each subgroup of participants. Each participant is represented in the point cloud (pink, control subjects; green, patients with bipolar disorder without psychotic features; patients with bipolar disorder and psychotic features (BD Psy–), blue; patients with schizophrenia (Scz; BD Psy+), purple. Mean of the masking threshold and the mean gFA in each group is represented by the dots with black outlines on the regression lines. Bottom, Mediation analysis with estimates and p values of mediated, direct, and total effects for CLFs and corpus callosum. Mean gFA of the CLFs and the corpus callosum significantly influenced the presence of psychotic symptoms but not that of the IFO. Mediated effects were significant, while direct effects were not, which means that the effect of cerebral connectivity on the advent of psychotic symptoms was fully mediated by the masking threshold.
